The Relationship between Anger Expression and Performance Score in Parents and Coaches: The Mediating Role of Self-Efficacy and Assertiveness
- PMID: 37047985
- PMCID: PMC10094228
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20075372
The Relationship between Anger Expression and Performance Score in Parents and Coaches: The Mediating Role of Self-Efficacy and Assertiveness
Abstract
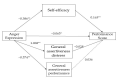
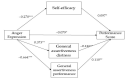
Background: Youth sport provides regular physical activity for millions of children. It is a global system, which includes coaches, referees, athletes, and parent spectators; consequently, the behavior of each member can influence the experiences of others. This study aimed to investigate the mediating role of self-efficacy and assertiveness in the relationship between the degree of anger expression and the performance children's score in a group of parents and coaches.
Methods: 200 parents (96 fathers, 104 mothers) and 200 coaches (119 males, 81 females) responded to the General Self-efficacy Scale, The Scale for Interpersonal Behavior, and the State-Trait Anger Expression Inventory-2; an indicator of performance was asked of each coach. The age range of parents was 28-59 years (M = 41.39, SD = 7.07), while that of coaches was 27-43 years (M = 35.91, SD = 3.35).
Results: Results revealed that self-efficacy and assertiveness were the direct and indirect predictors of performance score.
Conclusions: The study provided an understanding of the nature and magnitude of this profoundly interpersonal experience. Future studies may advance relevant education programs and effective interventions aimed at reducing angry expressions and lack of communication.
Keywords: children; coaching; parents; performance; physical activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Eime R.M., Young J.A., Harvey J.T., Charity M.J., Payne W.R. A systematic review of the psychological and social benefits of participation in sport for children and adolescents: Informing development of a conceptual model of health through sport. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2013;10:98–119. doi: 10.1186/1479-5868-10-98. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu X.Y., Han L.H., Zhang J.H., Luo S., Hu J.W., Sun K. The influence of physical activity, sedentary behavior on health-related quality of life among the general population of children and adolescents: A systematic review. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0187668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187668. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aston R. Physical Health and Well-Being in Children and Youth: Review of the Literature. OECD Publishing; Paris, France: 2018. OECD Education Working Papers (N. 170) - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

