The Glymphatic System May Play a Vital Role in the Pathogenesis of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 37048052
- PMCID: PMC10093707
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12070979
The Glymphatic System May Play a Vital Role in the Pathogenesis of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Narrative Review
Abstract
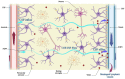
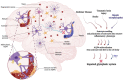
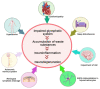
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a neurological complication of liver disease resulting in cognitive, psychiatric, and motor symptoms. Although hyperammonemia is a key factor in the pathogenesis of HE, several other factors have recently been discovered. Among these, the impairment of a highly organized perivascular network known as the glymphatic pathway seems to be involved in the progression of some neurological complications due to the accumulation of misfolded proteins and waste substances in the brain interstitial fluids (ISF). The glymphatic system plays an important role in the clearance of brain metabolic derivatives and prevents aggregation of neurotoxic agents in the brain ISF. Impairment of it will result in aggravated accumulation of neurotoxic agents in the brain ISF. This could also be the case in patients with liver failure complicated by HE. Indeed, accumulation of some metabolic by-products and agents such as ammonia, glutamine, glutamate, and aromatic amino acids has been reported in the human brain ISF using microdialysis technique is attributed to worsening of HE and correlates with brain edema. Furthermore, it has been reported that the glymphatic system is impaired in the olfactory bulb, prefrontal cortex, and hippocampus in an experimental model of HE. In this review, we discuss different factors that may affect the function of the glymphatic pathways and how these changes may be involved in HE.
Keywords: astrocytes; brain fluids; glymphatic system; hepatic encephalopathy; waste substances.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impaired brain glymphatic flow in experimental hepatic encephalopathy.J Hepatol. 2019 Jan;70(1):40-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.08.021. Epub 2018 Sep 8. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30201461 Free PMC article.
-
The role of glymphatic system in the cerebral edema formation after ischemic stroke.Exp Neurol. 2021 Jun;340:113685. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113685. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Exp Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33676917 Review.
-
Glymphatic System in the Central Nervous System, a Novel Therapeutic Direction Against Brain Edema After Stroke.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Aug 4;13:698036. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.698036. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34421575 Free PMC article.
-
A novel conceptual framework for the functionality of the glymphatic system.J Neurophysiol. 2023 May 1;129(5):1228-1236. doi: 10.1152/jn.00360.2022. Epub 2023 Apr 19. J Neurophysiol. 2023. PMID: 37073982 Review.
-
The glymphatic system.Handb Clin Neurol. 2025;209:161-170. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-443-19104-6.00006-1. Handb Clin Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40122623 Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling of age-related neurological disease: utility of zebrafish.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 May 3;16:1399098. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1399098. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38765773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rewiring of the glymphatic landscape in metabolic disorders.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2025 Aug;36(8):710-720. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2024.11.005. Epub 2024 Dec 4. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2025. PMID: 39638721 Review.
-
Ammonia-induced stress response in liver disease progression and hepatic encephalopathy.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Nov;21(11):774-791. doi: 10.1038/s41575-024-00970-9. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39251708 Review.
-
Sleep and Perivascular Spaces.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2023 Oct;23(10):607-615. doi: 10.1007/s11910-023-01293-z. Epub 2023 Aug 12. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37572227 Review.
-
The Role of Astrocytes in CNS Disorders: Historic and Contemporary Views.Cells. 2024 Aug 20;13(16):1388. doi: 10.3390/cells13161388. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39195276 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vigo M.B., Pérez M.J., De Fino F., Gómez G., Martínez S.A., Bisagno V., Di Carlo M.B., Scazziota A., Manautou J.E., Ghanem C.I. Acute acetaminophen intoxication induces direct neurotoxicity in rats manifested as astrogliosis and decreased dopaminergic markers in brain areas associated with locomotor regulation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019;170:113662. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.113662. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tevethia H.V., Choudhury A., Maiwall R., Mitra L., Saluja V., Singh P., Trigatia A., Kumar G., Thapar S., Sarin S.K. Noninvasive diagnosis of cerebral edema in patients of acute liver failure. Hepatol. Int. 2018;12:S614. doi: 10.1007/s12072-018-9852-3. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

