Gene Suppression Therapies in Hereditary Cerebellar Ataxias: A Systematic Review of Animal Studies
- PMID: 37048110
- PMCID: PMC10093402
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12071037
Gene Suppression Therapies in Hereditary Cerebellar Ataxias: A Systematic Review of Animal Studies
Abstract
Introduction: Hereditary cerebellar ataxias (HCAs) are a heterogenous group of neurodegenerative disorders associated with severe disability. Treatment options are limited and overall restricted to symptomatic approaches, leading to poor prognoses. In recent years, there has been extensive research on gene suppression therapies (GSTs) as a new hope for disease-modifying strategies. In this article, we aim to perform a review of in vivo studies investigating the efficacy and safety profile of GSTs in HCAs.
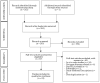
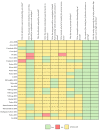
Methods: A structured PubMed® search on GSTs in HCAs from January 1993 up to October 2020 was performed. Inclusion and exclusion criteria were defined, and the selection process was conducted accordingly. The screening process was independently carried out by two authors and was initially based on title and abstract, followed by full-text reading. The risk-of-bias assessment was performed with SYRCLE's tool. A data extraction sheet was created to collect relevant information from each selected article.
Results: The initial search yielded 262 papers, of which 239 were excluded. An additional article was obtained following reference scrutiny, resulting in a total of 24 articles for final analysis. Most studies were not clear on the tools used to assess bias. In SCA1, SCA2, MJD/SCA3 and SCA7, RNA interference (iRNA) and antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) therapies proved to be well tolerated and effective in suppressing mutant proteins, improving neuropathological features and the motor phenotype. In SCA6, the phenotype was improved, but no investigation of adverse effects was performed. In FRDA, only the suppression efficacy of the electroporation of the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats associated with Cas9 enzyme system (CRISPR-Cas9) system was tested and confirmed.
Conclusion: The literature reviewed suggests that GSTs are well tolerated and effective in suppressing the targeted proteins, improving neuropathological features and the motor phenotype in vivo. Nonetheless, there is no guarantee that these results are free of bias. Moreover, further investigation is still needed to clarify the GST effect on HCAs such as FRDA, SCA6 and SCA2.
Keywords: Machado–Joseph disease; RNA interference; gene silencing; hereditary spinocerebellar degenerations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Spinocerebellar ataxias: from pathogenesis to recent therapeutic advances.Front Neurosci. 2024 Jun 4;18:1422442. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1422442. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38894941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered Metabolic Signaling and Potential Therapies in Polyglutamine Diseases.Metabolites. 2024 May 31;14(6):320. doi: 10.3390/metabo14060320. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38921455 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials