A Ratiometric Fluorescent Sensor Based on Silicon Quantum Dots and Silver Nanoclusters for Beef Freshness Monitoring
- PMID: 37048285
- PMCID: PMC10094156
- DOI: 10.3390/foods12071464
A Ratiometric Fluorescent Sensor Based on Silicon Quantum Dots and Silver Nanoclusters for Beef Freshness Monitoring
Abstract
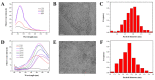
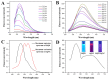
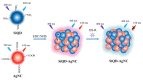
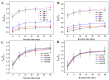
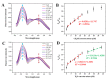
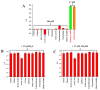
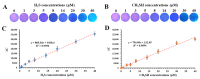
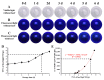
A ratiometric fluorescent sensor with hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and methanthiol (CH3SH) sensitivity was developed to real-time monitor beef freshness. A silicon quantum dots (SiQD) and silver nanoclusters (AgNC) complex, namely SiQD-AgNC, was used as the dual emission fluorescence materials. Due to the fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) effect between SiQD and AgNC, when the fluorescence of AgNC (610 nm) was quenched by H2S or CH3SH, the fluorescence of SiQD (468 nm) recovered, resulting in an increase of the fluorescent intensity ratio (I468/I610). I468/I610 showed a linear relationship with the H2S concentration within the concentration range of 1.125-17 μM, with a limit of detection (LOD) value of 53.6 nM. Meanwhile, I468/I610 presented two linear relationships with the CH3SH concentration within the concentration range of 1.125-17 μM and 23.375-38.25 μM, respectively, with a LOD value of 56.5 nM. The SiQD-AgNC complex was coated on a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) film to form a portable SiQD-AgNC/PVDF film sensor. This film showed purplish red-to-cyan color changes in response to H2S and CH3SH, with LOD values of 224 nM and 233 nM to H2S and CH3SH, respectively. When the film was used to monitor beef freshness at 4 °C, its fluorescent color gradually changed from purplish red to cyan. Hence, this study presented a new ratiometric fluorescent sensor for intelligent food packaging.
Keywords: beef freshness; fluorescent sensor; intelligent packaging; silicon quantum dots; silver nanoclusters.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors were not employed by the company Yixing Institute of Food and Biotechnology Co., Ltd. All authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yam K.L., Takhistov P.T., Miltz J. Intelligent packaging: Concepts and applications. J. Food Sci. 2005;70:0022–1147. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2005.tb09052.x. - DOI
-
- Bhargava N., Sharanagat V.S., Mor R.S., Kumar K. Active and intelligent biodegradable packaging films using food and food waste-derived bioactive compounds: A review. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2020;105:385–401. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2020.09.015. - DOI
-
- Zia J., Mancini G., Bustreo M., Zych A., Donno R., Athanassiou A., Fragouli D. Porous pH natural indicators for acidic and basic vapor sensing. Chem. Eng. J. 2021;403:126373. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126373. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 32102080, 31801631, 1601360061, 32150410347, 32272407/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- ZJ2022135/Zhejiang Postdoctoral Programs
- 2022NKY05/Postdoctoral project of Institute of Modern Agriculture and Health Care Industry of Wencheng
- BK20220058, BK20200103, BK2022011/Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- 202074/Foundation of Jiangsu Specially-Appointed Professor
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

