Composition, Organoleptic Characteristics, Fatty Acid Profile and Oxidative Status of Cow's Milk and White Cheese after Dietary Partial Replacement of Soybean Meal with Flaxseed and Lupin
- PMID: 37048415
- PMCID: PMC10093268
- DOI: 10.3390/ani13071159
Composition, Organoleptic Characteristics, Fatty Acid Profile and Oxidative Status of Cow's Milk and White Cheese after Dietary Partial Replacement of Soybean Meal with Flaxseed and Lupin
Abstract
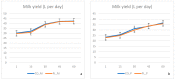
The effect of partial substitution of soybean meal by equal quantities of flaxseed and lupins in diets of Holstein dairy cows and heifers was investigated. A total of 6 animals (30 multiparous and 30 primiparous) were allocated into two equal groups in a randomised block design and fed control (group CO) or modified (group FL) TMR diets from three weeks prior to calving until day 40 postpartum. The TMR of group CO contained corn, barley, soybean meal, rapeseed cake, corn silage, and Lucerne hay, whereas in group FL equal quantities of whole flaxseed and lupins were used to replace 50% of the soybean meal in the TMR. All animals were fed twice daily with a daily allowance of 24 kg dry matter intake per animal. Milking was carried out three times daily and milk yield was recorded during every milking. Milk samples were analysed for chemical composition and SCC content. White cheeses were manufactured from bulk milk of each group at industrial level. Bulk milk and white cheese were analysed for chemical composition and fatty acid profile; cheese was also assessed for its organoleptic properties. Results indicate that milk yield did not differ among groups. Lipid oxidation values were similar among the groups, for both milk and cheese. However, FL inclusion resulted in lower (p < 0.05) protein carbonyls and higher (p < 0.05) phenolic compounds in both milk and cheese samples. Milk from the FL group had decreased palmitic (p < 0.05) and myristic (p < 0.05) and increased oleic (p < 0.05) and linolenic acid (p < 0.05) when compared to group CO. White cheese from group FL showed a decrease in saturated fatty acids (SFA) (p < 0.05), an increase in monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) (p < 0.05), and a higher increase in polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) (p < 0.05) when compared with that of group CO. The white cheese of cows fed diets with flaxseed and lupins showed compositional and organoleptic properties quite similar to control group cheese; aroma, texture, and color were acceptable and desirable in both cheeses. However, increased levels of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids were found in the cheese of FL fed animals. The substitution of soybean meal by flaxseed and lupins in diets of Holstein cows warrants further investigation, especially towards the production of cheese that meet the consumers' demand for novel and healthier dairy products.
Keywords: antioxidant status; dairy cows; flaxseed; lupins; milk fatty acids; organoleptic characteristics; soybean meal; white cheese.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Feeding Flaxseed and Lupins during the Transition Period in Dairy Cows: Effects on Production Performance, Fertility and Biochemical Blood Indices.Animals (Basel). 2023 Jun 13;13(12):1972. doi: 10.3390/ani13121972. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370482 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of corn meal or molasses with a soybean-sunflower meal mix or flaxseed meal on production, milk fatty acid composition, and nutrient utilization in dairy cows fed grass hay-based diets.J Dairy Sci. 2015 Jan;98(1):443-57. doi: 10.3168/jds.2014-8353. Epub 2014 Nov 14. J Dairy Sci. 2015. PMID: 25465544
-
Hepatic lipid metabolism in transition dairy cows fed flaxseed.J Dairy Sci. 2007 Oct;90(10):4780-92. doi: 10.3168/jds.2007-0066. J Dairy Sci. 2007. PMID: 17881701 Clinical Trial.
-
Dietary Grape Pomace Supplementation in Dairy Cows: Effect on Nutritional Quality of Milk and Its Derived Dairy Products.Foods. 2020 Feb 10;9(2):168. doi: 10.3390/foods9020168. Foods. 2020. PMID: 32050684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Seed and Co-Products Inclusion in Diets for Dairy Ruminants: A Review.Animals (Basel). 2021 Mar 17;11(3):856. doi: 10.3390/ani11030856. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803004 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- United States . Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2010 (No. 232) US Department of Health and Human Services; US Department of Agriculture; Washington, DC, USA: 2010. Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee.
-
- Vargas-Bello-Pérez E., Geldsetzer-Mendoza C., Morales M.S., Toro-Mujica P., Fellenberg M.A., Ibáñez R.A., Garnsworthy P.C. Effect of olive oil in dairy cow diets on the fatty acid profile and sensory characteristics of cheese. Int. Dairy J. 2018;85:8–15. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2018.04.006. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

