Effect of Growth Factors and Hormones during In Vitro Growth Culture of Cumulus-Oocyte-Complexes Derived from Small Antral Follicles in Pigs
- PMID: 37048462
- PMCID: PMC10093161
- DOI: 10.3390/ani13071206
Effect of Growth Factors and Hormones during In Vitro Growth Culture of Cumulus-Oocyte-Complexes Derived from Small Antral Follicles in Pigs
Abstract
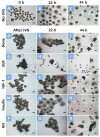
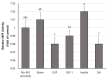
This study evaluated the effect of various growth factors and hormones in an in vitro growth (IVG) medium on the in vitro maturation (IVM) and developmental competence of oocytes derived from small antral follicles (SAFs) in pigs. Cumulus-oocyte complexes (COCs) derived from SAFs were either untreated or treated with epidermal growth factor (EGF), insulin-like factor-1 (IGF-1), insulin, or growth hormone (GH) for 2 days of IVG. Following IVG, COCs were cultured for maturation, and IVM oocytes were induced for parthenogenesis (PA). During IVG, the nuclear maturation of oocytes was significantly increased by the insulin treatment compared to other treatments. Moreover, the insulin treatment significantly increased blastocyst formation after PA relative to the No-IVG, control, EGF, and GH treatments. The cumulus expansion score after IVG-IVM was significantly higher in the insulin group than in the other groups. The glutathione (GSH) contents in IVM oocytes were increased through treatment with IGF, insulin, and GH compared to those of No-IVG oocytes. The level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in IVM oocytes in all treatment groups was significantly lower after IVG culture than in the No-IVG group. The maturation-promoting factor (MPF) activity after IVM in the insulin-treated oocytes was significantly higher than that of the oocytes treated with EGF, IGF-1, and GH. In conclusion, this study demonstrates that insulin treatment during IVG culture improves the maturational and developmental competence of oocytes derived from SAFs in pigs through its effect on cumulus cell expansion and cytoplasmic microenvironments, such as GSH, ROS, and MPF activity.
Keywords: growth factor; in vitro growth culture; insulin; pig; small antral follicle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Supplement of cilostamide in growth medium improves oocyte maturation and developmental competence of embryos derived from small antral follicles in pigs.Theriogenology. 2017 Mar 15;91:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2016.12.015. Epub 2016 Dec 18. Theriogenology. 2017. PMID: 28215673
-
In vitro growth culture in a medium with reduced sodium chloride improves maturation and developmental competence of pig oocytes derived from small antral follicles.Theriogenology. 2021 Apr 15;165:37-43. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.12.018. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Theriogenology. 2021. PMID: 33639366
-
Epidermal growth factor enhances preimplantation developmental competence of maturing mouse oocytes.Hum Reprod. 1999 Dec;14(12):3060-8. doi: 10.1093/humrep/14.12.3060. Hum Reprod. 1999. PMID: 10601097
-
Role of growth hormone and growth hormone receptor in oocyte maturation.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2002 Nov 29;197(1-2):173-8. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(02)00270-8. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 12431810 Review.
-
Despite the donor's age, human adipose-derived stem cells enhance the maturation and development rates of porcine oocytes in a co-culture system.Theriogenology. 2018 Jul 15;115:57-64. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2017.12.024. Epub 2017 Dec 12. Theriogenology. 2018. PMID: 29709724 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Growth of Mammalian Follicles and Oocytes.Animals (Basel). 2024 Apr 30;14(9):1355. doi: 10.3390/ani14091355. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38731360 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hyun S.H., Lee G.S., Kim D.Y., Kim H.S., Lee S.H., Kim S., Lee E.S., Lim J.M., Kang S.K., Lee B.C., et al. Effect of maturation media and oocytes derived from sows or gilts on the development of cloned pig embryos. Theriogenology. 2003;59:1641–1649. doi: 10.1016/S0093-691X(02)01211-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lee J., Kim E., Hwang S.U., Cai L., Kim M., Choi H., Oh D., Lee E., Hyun S.H. Effect of D-Glucuronic Acid and N-acetyl-D-Glucosamine Treatment during In Vitro Maturation on Embryonic Development after Parthenogenesis and Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer in Pigs. Animals. 2021;11:1034. doi: 10.3390/ani11041034. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

