Crayfish Research: A Global Scientometric Analysis Using CiteSpace
- PMID: 37048496
- PMCID: PMC10093174
- DOI: 10.3390/ani13071240
Crayfish Research: A Global Scientometric Analysis Using CiteSpace
Retraction in
-
RETRACTED: Azra et al. Crayfish Research: A Global Scientometric Analysis Using CiteSpace. Animals 2023, 13, 1240.Animals (Basel). 2024 Nov 13;14(22):3259. doi: 10.3390/ani14223259. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39535122 Free PMC article.
Abstract
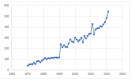
A scientometric analysis was conducted to investigate the trends and development of crayfish research in terms of literature published, author, affiliation, and countries' collaborative networks, as well as the co-citation dataset (e.g., author, article, and keywords). The study analyzed 12,039 bibliographic datasets from the Web of Science, using CiteSpace as a tool for the co-citation analysis. The study revealed extraordinary increases in publication trends, with a total of 21,329 authors involved in approximately 80% of countries around the world (163/195) having conducted crayfish research. Unsurprisingly, countries such as the USA and China, followed by European countries, were among the top countries that have published crayfish-related studies. The findings also indicated that "invasive crayfish" was the world's top keyword for crayfish research. Crayfish species are important for both environmental sustainability (invasiveness and species composition) and social wellbeing (aquaculture), which provides directions for research, philanthropic, academic, government, and non-government organizations regarding how to invest limited resources into policies, programs, and research towards the future management of this species. Our study concluded that strategic collaboration among authors, institutions, and countries would be vital to tackle the issue of invasive crayfish species around the world.
Keywords: aquaculture; aquatic organism; crayfish; environmental factors; invasive.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this article.
Figures



References
-
- Reynolds J., Souty-Grosset C., Richardson A. Ecological roles of crayfish in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. Freshw. Crayfish. 2013;19:197–218. doi: 10.5869/fc.2013.v19-2.197. - DOI
-
- Emery-Butcher H.E., Beatty S.J., Robson B.J. The impacts of invasive ecosystem engineers in freshwaters: A review. Freshw. Biol. 2020;65:999–1015. doi: 10.1111/fwb.13479. - DOI
-
- Haubrock P.J., Oficialdegui F.J., Zeng Y., Patoka J., Yeo D.C., Kouba A. The redclaw crayfish: A prominent aquaculture species with invasive potential in tropical and subtropical biodiversity hotspots. Rev. Aquac. 2021;13:1488–1530. doi: 10.1111/raq.12531. - DOI
-
- Manenti R., Ghia D., Fea G., Ficetola G.F., Padoa-Schioppa E., Canedoli C. Causes and consequences of crayfish extinction: Stream connectivity, habitat changes, alien species and ecosystem services. Freshw. Biol. 2019;64:284–293. doi: 10.1111/fwb.13215. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

