Causal Link between Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Fistula: Evidence from Mendelian Randomization Study
- PMID: 37048564
- PMCID: PMC10095427
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12072482
Causal Link between Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Fistula: Evidence from Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
Background: Previous observational studies have found that fistulas are common in Crohn's disease (CD) and less common in ulcerative colitis (UC). However, some patients have a fistula before diagnosis. Based on retrospective analysis, it was not possible to determine whether there was a bi-directional causal relationship between inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and fistulas.
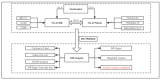
Methods: Data were extracted from the open GWAS database; 25,042 cases and 34,915 controls were included for IBD, and 6926 cases and 30,228 controls were included for fistula. Two-sample Mendelian randomization and multivariable Mendelian randomization were used in combination to determine the causal relationship between IBD and fistula.
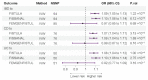
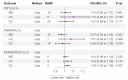
Results: Forward MR showed that IBD increased the risk of colonic or urogenital fistula (FISTULA) (OR: 1.09, 95% CI: 1.05 to 1.13, p = 1.22 × 10-6), mainly associated with fissure and fistula of the anal and rectal regions (FISSANAL) (OR:1.10, 95% CI:1.06 to 1.14, p = 6.12 × 10-8), but not with fistulas involving the female genital tract (FEMGENFISTUL) (OR:0.97, 95% CI: 0.85 to 1.11, p = 0.669). Furthermore, both UC and CD increased the risk of FISTULA. However, after adjusting by MVMR, only CD increased the risk of FISTULA (OR: 1.06, 95% CI: 1.02 to 1.11, p = 0.004), and UC did not increase the risk of FISTULA (OR: 1.01, 95% CI: 0.95 to 1.06, p = 0.838). Reverse MR showed that fistulas did not increase the risk of IBD.
Conclusion: Our study confirms it is CD, rather than UC, that casually leads to an increased risk of fistula, but fistulas do not increase the risk of IBD.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; fistula; genetic epidemiology; inflammatory bowel disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ng S.C., Shi H.Y., Hamidi N., Underwood F.E., Tang W., Benchimol E.I., Panaccione R., Ghosh S., Wu J.C.Y., Chan F.K.L., et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: A systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet. 2017;390:2769–2778. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32448-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Geldof J., Iqbal N., LeBlanc J.F., Anandabaskaran S., Sawyer R., Buskens C., Bemelman W., Gecse K., Lundby L., Lightner A.L., et al. Classifying perianal fistulising Crohn’s disease: An expert consensus to guide decision-making in daily practice and clinical trials. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022;7:576–584. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00007-3. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

