Comparison of Short- and Long-Term Effectiveness between Anti-TNF and Ustekinumab after Vedolizumab Failure as First-Line Therapy in Crohn's Disease: A Multi-Center Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 37048587
- PMCID: PMC10095015
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12072503
Comparison of Short- and Long-Term Effectiveness between Anti-TNF and Ustekinumab after Vedolizumab Failure as First-Line Therapy in Crohn's Disease: A Multi-Center Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: The effectiveness of anti-TNF or ustekinumab (UST) as a second-line biologic after vedolizumab (VDZ) failure has not yet been described.
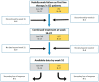
Aims and methods: In this retrospective multicenter cohort study, We aim to investigate the effectiveness of anti-TNF and UST as second-line therapy in patients with Crohn's disease (CD) who failed VDZ as a first-line treatment. The primary outcome was clinical response at week 16-22. Secondary outcomes included the rates of clinical remission, steroid-free clinical remission, CRP normalization, and adverse events.
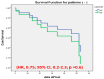
Results: Fifty-nine patients who failed on VDZ as a first-line treatment for CD were included; 52.8% patients received anti-TNF and 47.2% UST as a second-line therapy. In initial period (Week 16-22), the clinical response and remission rate was similar between both groups: 61.2% vs. 68%, p = 0.8 and 48.3% vs. 56%, p = 0.8 on anti-TNF and UST therapy, respectively. Furthermore, in the maintenance period the rate was similar: 75% vs. 82.3%, p = 0.8 and 62.5% vs. 70.5%, p = 0.8, respectively. Of the patients, 12 out of the 59 stopped the therapy, without a significant difference between the two groups (p = 0.6).
Conclusion: Second-line biological therapy after VDZ failure therapy was effective in >60% of the patients with CD. No differences in effectiveness were detected between the use of anti-TNF and UST as a second line.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; anti-TNF; drug positioning; treatment failure; treatment response; ustekinumab; vedolizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
Ahmad Albshesh—received speaking fees from Takeda; Stephan Vavricka—has received consulting fees, speakers honorary and unrestricted research grants from Abbott, Alfasigma, Amgen, Arenapharm, Falk Pharma GmbH, Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Gilead, iQuone, Janssen, MSD, Permamed, Pfizer Inc, Sanofi-Aventis, Takeda, Tillotts, UCB, and Vifor; Eran Zittan—received research support and consulting fees from Janssen, AbbVie, Takeda, Neopharm, Celgene and Pfizer; David Drobne—has served as a speaker, a consultant and an advisory board member for MSD, Abbvie, Takeda, Pfizer, Janssen, and Krka; Alessandro Armuzzi—consulting, advisory board and/or lecture fees and/or research support: AbbVie, Allergan, Amgen, Arena, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Ferring, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, MSD, Mylan, Novartis, Pfizer, Protagonist-Therapeutics, Roche, Samsung Bioepis, Sandoz, Takeda; Triana lobaton—Financial support for research from Abbvie, Viatris, MSD, Mundipharma, Biogen, Janssen, Pfizer and Takeda; Speaker fees from Ferring, MSD, Abbvie, Janssen, Amgen, Fresenius Kabi, Galapagos, Viatrisand Takeda; Consultancy fee from Janssen, Galapagos, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb Fresenius Kabiand Takeda; Nitsan Maharshak—has received speaking and/or consulting fees from Pfizer, Takeda, Janssen, Ferring, BiomX, BMS, Nestle and grant support from Takeda, Janssen, Abbott, Abbvie, Pfizer, BMS, Nestle, Trobix; Henit Yanai: reports institutional research grants from Pfizer and the ISF; consulting fees from Abbvie, Janssen, Pfizer, and Takeda; honoraria for lectures from Abbvie, Janssen, Pfizer, and Takeda; participation in a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board from Abbvie, Pfizer, and Takeda; Shomron Ben-Horin—consulting and advisory board fees and/or research support—Abbvie, MSD, Janssen, Takeda, and CellTrion; Uri Kopylov—research support- Jannsen Medtronic Takeda, advisory and speaker fees- Abbvie BMS Janssen Medtronic Novartis Pfizer Takeda. All other authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures
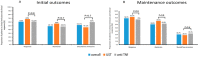

Similar articles
-
Ustekinumab is associated with superior treatment persistence but not with higher remission rates versus vedolizumab in patients with refractory Crohn's disease: results from a multicentre cohort study.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2022 Dec 26;15:17562848221144349. doi: 10.1177/17562848221144349. eCollection 2022. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36600684 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term effectiveness and safety of ustekinumab and vedolizumab in elderly and non-elderly patients with Crohn's disease: a comparative study.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2024 Nov 19;17:17562848241299752. doi: 10.1177/17562848241299752. eCollection 2024. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39569055 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Third-Class Biologic Treatment in Crohn's Disease: A Multi-Center Retrospective Cohort Study.J Clin Med. 2021 Jun 29;10(13):2914. doi: 10.3390/jcm10132914. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34209880 Free PMC article.
-
Ustekinumab or Vedolizumab after Failure of Anti-TNF Agents in Crohn's Disease: A Review of Comparative Effectiveness Studies.J Clin Med. 2024 Apr 10;13(8):2187. doi: 10.3390/jcm13082187. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38673459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic review with meta-analysis: the effectiveness of either ustekinumab or vedolizumab in patients with Crohn's disease refractory to anti-tumour necrosis factor.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Feb;55(4):380-388. doi: 10.1111/apt.16714. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34854100
Cited by
-
IBD Patients with Primary or Secondary Nonresponse to Ustekinumab Benefit from Dose Escalation or Reinduction.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 9;13(14):3993. doi: 10.3390/jcm13143993. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39064033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Superior persistence of ustekinumab compared to anti-TNF in vedolizumab-experienced inflammatory bowel diseases patients: a real-world cohort study.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Dec 31;24(1):483. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03577-1. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39741232 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stidham R.W., Lee T.C.H., Higgins P.D.R., Deshpande A.R., Sussman D.A., Singal A.G., Elmunzer B.J., Saini S.D., Vijan S., Waljee A.K. Systematic review with network meta-analysis: The efficacy of anti-TNF agents for the treatment of Crohn’s disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014;39:1349–1362. doi: 10.1111/apt.12749. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stidham R.W., Lee T.C.H., Higgins P.D.R., Deshpande A.R., Sussman D.A., Singal A.G., Waljee A.K. Effects of vedolizumab induction therapy for patients with Crohn’s disease in whom tumor necrosis factor antagonist treatment failed. Gastroenterology. 2014;147:618–627.e3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

