Sex, Age, and Comorbidities Are Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection, COVID-19 Severity, and Fatal Outcome in a Mexican Population: A Retrospective Multi-Hospital Study
- PMID: 37048758
- PMCID: PMC10095205
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12072676
Sex, Age, and Comorbidities Are Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection, COVID-19 Severity, and Fatal Outcome in a Mexican Population: A Retrospective Multi-Hospital Study
Abstract
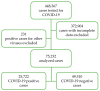
People with comorbidities and the male sex are at a higher risk of developing severe COVID-19. In the present study, we aim to investigate the associated factors for infection, severity, and death due to COVID-19 in a population from Nuevo León, México. Epidemiological COVID-19 data were collected from 65 hospitals from December 2020 to May 2022. A total of 75,232 cases were compiled from which 25,722 cases were positive for SARS-CoV-2. Male sex, older age, diabetes, obesity, and hypertension were associated with infection. In addition to the above-mentioned factors, renal disease, cardiovascular disease, and immunosuppression were found to be associated with increased COVID-19 severity. These factors, as well as neurological diseases, are also associated with death due to COVID-19. When comparing the different variants of SARs-CoV-2, the variant B1.1.519 increased the probability of death by 2.23 times compared to the AY.20 variant. Male sex, older age, diabetes, obesity, and hypertension are associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection, severity, and death. Along with the aforementioned comorbidities, renal disease, cardiovascular disease, and immunosuppression are also associated with severity and death. Another factor associated with death is the presence of neurological disease. The SARS-CoV-2 B1.1.519 variant increases the odds of death compared to the SARS-CoV-2 AY.20 variant.
Keywords: COVID-19; Mexico; SARS-CoV-2; association; death; severity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Determinants of survival after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in Mexican outpatients and hospitalised patients.Public Health. 2020 Dec;189:66-72. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2020.09.014. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33166857 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors for SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Pneumonia, Intubation, and Death in Northeast Mexico.Front Public Health. 2021 Jul 5;9:645739. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.645739. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34291023 Free PMC article.
-
Comorbidities and laboratory parameters associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection severity in patients from the southeast of Mexico: a cross-sectional study.F1000Res. 2022 Jan 6;11:10. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.74023.2. eCollection 2022. F1000Res. 2022. PMID: 35464048 Free PMC article.
-
[Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of the COVID-19 epidemic in Mexico: Quintana Roo case].Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2022 Oct 25;60(6):657-665. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2022. PMID: 36283034 Free PMC article. Review. Spanish.
-
Thyroid autoimmunity and SARS-CoV-2 infection: Report of a large Italian series.Autoimmun Rev. 2022 Nov;21(11):103183. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2022.103183. Epub 2022 Aug 23. Autoimmun Rev. 2022. PMID: 36007802 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Hypertension and Antihypertensive Treatment on COVID-19 Severity: A Retrospective Observational Study in Ternopil Region, Ukraine.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2025 Jun 25;21:995-1007. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S527151. eCollection 2025. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2025. PMID: 40625672 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus and Hypertension Among COVID-19 Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study Exploring Associations With Sociodemographic and Biological Factors in Rajshahi Division, Bangladesh.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 19;8(8):e71183. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.71183. eCollection 2025 Aug. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40843391 Free PMC article.
-
Occult Serologically Confirmed Cases of SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus among the General Population in the Era of the Fourth Vaccination.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 22;13(16):4953. doi: 10.3390/jcm13164953. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39201097 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the complex interplay of age, comorbidities, and multimorbidities in COVID-19 disease progression: Clinical implications and future perspectives.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 2;10(15):e35570. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35570. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170247 Free PMC article.
-
Barcoded SARS-CoV-2 viruses define the impact of duration and route of exposure on the transmission bottleneck in a hamster model.Sci Adv. 2025 Jan 17;11(3):eads2927. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ads2927. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 39813353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . COVID-19 Dashboard. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2020. [(accessed on 14 February 2023)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/info.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous