New Approach to Determine the Activity Concentration Index in Cements, Fly Ashes, and Slags on the Basis of Their Chemical Composition
- PMID: 37048970
- PMCID: PMC10095990
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16072677
New Approach to Determine the Activity Concentration Index in Cements, Fly Ashes, and Slags on the Basis of Their Chemical Composition
Abstract
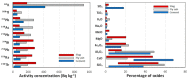
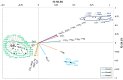
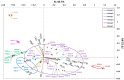
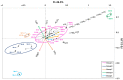
The manufacture of Portland cement entails high energy and environmental costs, and various solutions have been implemented in recent years to mitigate this negative impact. These solutions include improvements in the manufacture of cement clinker or the use of supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs), such as fly ash (FA) or slag as a replacement for a portion of the clinker in cement. The incorporation of these SCMs in cement may increase its radiological content as they are naturally occurring radioactive materials (NORMs). The Activity Concentration Index (ACI) is a screening tool established in the European EURATOM Directive 2013/59 to determine the radiation protection suitability of a final construction material. The ACI is determined by the activity concentrations of 226Ra, 232Th and 40K, usually determined by gamma spectrometry. The methodology of gamma spectrometry is accurate and appropriate, but this technique is not available in all laboratories. For this reason, and taking into account that there is a relationship between the chemical and radiological composition of these building materials, a new approach is proposed to determine the radiological content of these materials from a chemical analysis such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF). In this paper, principal component analysis (PCA) is used to establish the relationships between the chemical composition and radiological content of cements, FAs, and slags of different natures. Through PCA it was possible to group the cements based on two variables: CaO content and Fe2O3-Al2O3-TiO2 content. A lower correlation was observed for the FAs and slags, as the sample scores were centered around the origin of the coordinates and showed greater dispersion than the cements. The clusters obtained in the HJ-Biplots allowed the determination, using multiple regression, of models relating the activity concentration of 226Ra, 232Th (212Pb), and 40K to the oxide percentages obtained for the three matrices studied. The models were validated using five cements, one FA and one slag with relative percentage deviations (RSD(%)) equal to or less than 30% for 89% of the activity concentrations and 100% of the ACI determined.
Keywords: HJ-Biplot; NORM; activity concentration index; cement; fly ash; slag.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- EU . Council Directive 2013/59/Euratom of 5 Dec. Laying down Basic Safety Standards for Protection against the Dangers Arising from Exposure to Ionising Radiation, and Repealing Directives 89/618/Euratom, 90/641/Euratom, 96/29/Euratom, 97/43/Euratom and 2003/122/Euratom. Volume 57 European Commission; Brussels, Belgium: 2013.
-
- Suárez-Navarro J.A., Lanzón M., Moreno-Reyes A.M., Gascó C., Alonso M.M., Blanco-Varela M.T., Puertas F. Radiological behaviour of pigments and water repellents in cement-based mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019;225:879–885. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.07.271. - DOI
-
- Suárez-Navarro J.A., Moreno-Reyes A.M., Gascó C., Alonso M.M., Puertas F. Gamma spectrometry and LabSOCS-calculated efficiency in the radiological characterisation of quadrangular and cubic specimens of hardened portland cement paste. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020;171:108709. doi: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2020.108709. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

