Synthesis of Natural-Inspired Materials by Irradiation: Data Mining from the Perspective of Their Functional Properties in Wastewater Treatment
- PMID: 37048979
- PMCID: PMC10096124
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16072686
Synthesis of Natural-Inspired Materials by Irradiation: Data Mining from the Perspective of Their Functional Properties in Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
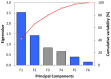
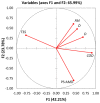
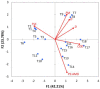
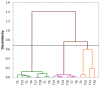
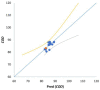
The present study is focused on assessing the interrelation of variables involved in the synthesis of natural-inspired copolymers by electron beam grafting while taking the functionality of the resulting materials into account. In this respect, copolymers of starch-graft-polyacrylamide (St-g-PAM) were synthesized by irradiation, and their flocculation efficiency regarding the total suspended solids (TSS), chemical oxygen demand (COD), and fatty matters (FM) was tested in coagulation-flocculation experiments at laboratory scale on wastewater from the oil industry. Data mining involved approaches related to the association (correlation and dimensionality reduction with principal component analysis (PCA)), clustering by agglomerative hierarchical clustering (AHC), classifying by classification and regression tree (CART), and prediction (decision tree prediction, multiple linear regression (MLR), and principal component regression (PCR)) of treatments applied with the variation of the monomer concentration, irradiation dose, and dose rate. The relationship mining proved that the level of COD was significantly affected by the irradiation dose and monomer concentration, and FM was mainly affected by the dose rate (significance level = 0.05). TSS showed the highest negative correlation with the tested variables. Moreover, the consequences of MLR demonstrated an acceptable accuracy (mean absolute percentage error < 5%) for COD and FM; meanwhile, linear modeling together with the consequences of PCA in the structure of PCR could help to simplify and improve the prediction accuracy of equations.
Keywords: biopolymer; copolymerization; correlation; feature selection; flocculant; functionality; prediction; principal components; statistical techniques.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Water-Soluble Starch-Based Copolymers Synthesized by Electron Beam Irradiation: Physicochemical and Functional Characterization.Materials (Basel). 2022 Jan 29;15(3):1061. doi: 10.3390/ma15031061. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35161009 Free PMC article.
-
Olive mill wastewater pretreatment by combination of filtration on olive stone filters and coagulation-flocculation.Environ Technol. 2019 Jul;40(16):2135-2146. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2018.1439106. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Environ Technol. 2019. PMID: 29421956
-
Plasma-induced synthesis of chitosan-g-polyacrylamide and its flocculation performance for algae removal.Environ Technol. 2019 Mar;40(8):954-968. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2017.1414312. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Environ Technol. 2019. PMID: 29210322
-
Cactus juice as bioflocculant in the coagulation-flocculation process for industrial wastewater treatment: a comparative study with polyacrylamide.Water Sci Technol. 2014;70(7):1175-81. doi: 10.2166/wst.2014.328. Water Sci Technol. 2014. PMID: 25325541
-
Upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor--a review.Indian J Environ Health. 2001 Apr;43(2):1-82. Indian J Environ Health. 2001. PMID: 12397675 Review.
References
-
- Khalid S., Shahid M., Bibi I., Sarwar T., Shah A.H., Niazi N.K. A review of environmental contamination and health risk assessment of wastewater use for crop irrigation with a focus on low and high-income countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2018;15:895. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15050895. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoang S.A., Bolan N., Madhubashani A.M., Vithanage M., Perera V., Wijesekara H., Wang H., Srivastava P., Kirkham M.B., Mickan B.S., et al. Treatment processes to eliminate potential environmental hazards and restore agronomic value of sewage sludge: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2022;293:118564. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118564. - DOI - PubMed
-
- The C.Y., Budiman P.M., Shak K.P., Wu T.Y. Recent advancement of coagulation–flocculation and its application in wastewater treatment. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016;55:4363–4389. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.5b04703. - DOI
-
- Qi Y., Thapa K.B., Hoadley A.F. Application of filtration aids for improving sludge dewatering properties–a review. Chem. Eng. J. 2011;171:373–384. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.04.060. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

