Hydrothermal Reduction of CO2 to Value-Added Products by In Situ Generated Metal Hydrides
- PMID: 37049198
- PMCID: PMC10096008
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16072902
Hydrothermal Reduction of CO2 to Value-Added Products by In Situ Generated Metal Hydrides
Abstract
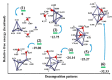
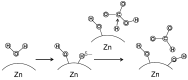
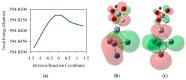
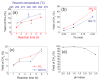
An integrated process by coupling hydrothermal reactions, including CO2 reduction and H2O dissociation with metals, is proposed. The hydrogen could be rapidly produced under hydrothermal conditions, owing to the special characteristics of high temperature water, generating metal hydrides as intermediates. Hydrogen production from the H2O dissociation under hydrothermal conditions is one of the most ideal processes due to its environmentally friendly impact. Recent experimental and theoretical studies on the hydrothermal reduction of CO2 to value-added products by in situ generated metal hydrides are introduced, including the production of formic acid, methanol, methane, and long-chain hydrocarbons. These results indicate that this process holds promise in respect to the conversion of CO2 to useful chemicals and fuels, and for hydrogen storage, which could help alleviate the problems of climate change and energy shortage.
Keywords: CO2; hydrogen storage; hydrogenation; hydrothermal reduction; metal hydrides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



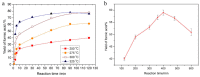
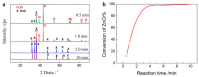

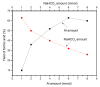


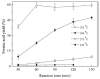



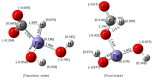

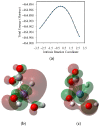


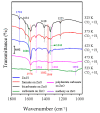
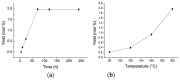



References
-
- Song J.W., Yang Y., Yao G.D., Zhong H., He R.T., Jin B.B., Jing Z.Z., Jin F.M. Highly Efficient Synthesis of Hydrogen Storage Material of Formate from Bicarbonate and Water with General Zn Powder. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017;56:6349–6357. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.7b00190. - DOI
-
- Iqbal M., Azam M., Naeem M., Khwaja A.S., Anpalagan A. Optimization classification, algorithms and tools for renewable energy: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014;39:640–650. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2014.07.120. - DOI
-
- Belmonte N., Girgenti V., Florian P., Peano C., Luetto C., Rizzi P., Baricco M. A comparison of energy storage from renewable sources through batteries and fuel cells: A case study in Turin, Italy. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 2016;41:21427–21438. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.07.260. - DOI
-
- Allouhi A., El Fouih Y., Kousksou T., Jamil A., Zeraouli Y., Mourad Y. Energy consumption and efficiency in buildings: Current status and future trends. J. Clean. Prod. 2015;109:118–130. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.05.139. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

