Synergistic Effects of Magnetic Z-Scheme g-C3N4/CoFe2O4 Nanofibres with Controllable Morphology on Photocatalytic Activity
- PMID: 37049235
- PMCID: PMC10096916
- DOI: 10.3390/nano13071142
Synergistic Effects of Magnetic Z-Scheme g-C3N4/CoFe2O4 Nanofibres with Controllable Morphology on Photocatalytic Activity
Abstract
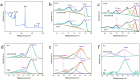
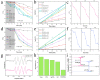
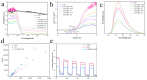
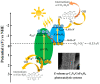
The rational design of interfacial contacts plays a decisive role in improving interfacial carrier transfer and separation in heterojunction photocatalysts. In Z-scheme photocatalysts, the recombination of photogenerated electron-hole pairs is prevented so that the redox capacity is maintained. Here, one-dimensional graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4)/CoFe2O4 fibres were synthesised as a new type of magnetic Z-scheme visible-light photocatalyst. Compared with pure g-C3N4 and CoFe2O4, the prepared composite photocatalysts showed considerably improved performance for the photooxidative degradation of tetracycline and methylene blue. In particular, the photodegradation efficiency of the g-C3N4/CoFe2O4 fibres for methylene blue was approximately two and seven times those of g-C3N4 and CoFe2O4, respectively. The formation mechanism of the Z-scheme heterojunctions in the g-C3N4/CoFe2O4 fibres was investigated using photocurrent spectroscopy and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. We proposed that one of the reasons for the improved photodegradation performance is that the charge transport path in one-dimensional materials enables efficient photoelectron and hole transfer. Furthermore, the internal electric field of the prepared Z-scheme photocatalyst enhanced visible-light absorption, which provided a barrier for photoelectron-hole pair recombination.
Keywords: Z-scheme; magnetic; nanofibers; photocatalyst.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Rational design direct Z-scheme BiOBr/g-C3N4 heterojunction with enhanced visible photocatalytic activity for organic pollutants elimination.RSC Adv. 2020 Jan 29;10(8):4681-4689. doi: 10.1039/c9ra10146b. eCollection 2020 Jan 24. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35495249 Free PMC article.
-
Boosted photocatalytic performance of cobalt ferrite anchored g-C3N4 nanocomposite toward various emerging environmental hazardous pollutants degradation: insights into stability and Z-scheme mechanism.Environ Geochem Health. 2024 Jul 11;46(8):302. doi: 10.1007/s10653-024-02085-1. Environ Geochem Health. 2024. PMID: 38990227
-
Construction of Z-scheme g-C3N4 / MnO2 /GO ternary photocatalyst with enhanced photodegradation ability of tetracycline hydrochloride under visible light radiation.Environ Res. 2021 Sep;200:111427. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111427. Epub 2021 May 29. Environ Res. 2021. PMID: 34062202
-
Graphitic Carbon Nitride/Zinc Oxide-Based Z-Scheme and S-Scheme Heterojunction Photocatalysts for the Photodegradation of Organic Pollutants.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 9;24(19):15021. doi: 10.3390/ijms241915021. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in ternary Z-scheme photocatalysis on graphitic carbon nitride based photocatalysts.Front Chem. 2024 Apr 3;12:1359895. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1359895. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 38633985 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Ag-Bridged Z-Scheme CdS/Ag/Bi2WO6 Heterojunction: Excellent Photocatalytic Performance and Insight into the Underlying Mechanism.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Feb 4;14(3):315. doi: 10.3390/nano14030315. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38334586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen C., Zhang J., Xiong X., Lin J., Yang S., Xi J., Kong Z. A novel Z-type multidimensional FeSe2/CuSe heterojunction photocatalyst with high photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical performance. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2022;47:28879–28893. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.06.219. - DOI
-
- Bukhari S., Shah A.A., Bhatti M.A., Tahira A., Channa I.A., Shah A.K., Chandio A.D., Mahdi W.A., Alshehri S., Ibhupoto Z.H., et al. Psyllium-Husk-Assisted Synthesis of ZnO Microstructures with Improved Photocatalytic Properties for the Degradation of Methylene Blue (MB) Nanomaterials. 2022;12:3568. doi: 10.3390/nano12203568. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

