Infrared Photodetection from 2D/3D van der Waals Heterostructures
- PMID: 37049263
- PMCID: PMC10096675
- DOI: 10.3390/nano13071169
Infrared Photodetection from 2D/3D van der Waals Heterostructures
Abstract
An infrared photodetector is a critical component that detects, identifies, and tracks complex targets in a detection system. Infrared photodetectors based on 3D bulk materials are widely applied in national defense, military, communications, and astronomy fields. The complex application environment requires higher performance and multi-dimensional capability. The emergence of 2D materials has brought new possibilities to develop next-generation infrared detectors. However, the inherent thickness limitations and the immature preparation of 2D materials still lead to low quantum efficiency and slow response speeds. This review summarizes 2D/3D hybrid van der Waals heterojunctions for infrared photodetection. First, the physical properties of 2D and 3D materials related to detection capability, including thickness, band gap, absorption band, quantum efficiency, and carrier mobility, are summarized. Then, the primary research progress of 2D/3D infrared detectors is reviewed from performance improvement (broadband, high-responsivity, fast response) and new functional devices (two-color detectors, polarization detectors). Importantly, combining low-doped 3D and flexible 2D materials can effectively improve the responsivity and detection speed due to a significant depletion region width. Furthermore, combining the anisotropic 2D lattice structure and high absorbance of 3D materials provides a new strategy in high-performance polarization detectors. This paper offers prospects for developing 2D/3D high-performance infrared detection technology.
Keywords: 2D materials; 2D/3D infrared detectors; bulk infrared materials; heterojunction; infrared detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
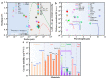
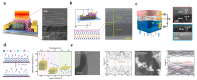
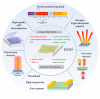
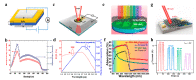
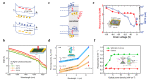
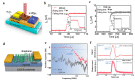
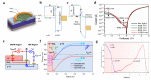
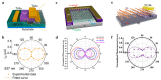
Similar articles
-
Tellurium/Bismuth Selenide van der Waals Heterojunction for Self-Driven, Broadband Photodetection and Polarization-Sensitive Application.Small. 2025 Feb;21(6):e2407830. doi: 10.1002/smll.202407830. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Small. 2025. PMID: 39703020
-
HgCdTe/black phosphorus van der Waals heterojunction for high-performance polarization-sensitive midwave infrared photodetector.Sci Adv. 2022 May 13;8(19):eabn1811. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn1811. Epub 2022 May 11. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35544556 Free PMC article.
-
Picosecond electrical response in graphene/MoTe2 heterojunction with high responsivity in the near infrared region.Fundam Res. 2021 Nov 9;2(3):405-411. doi: 10.1016/j.fmre.2021.09.018. eCollection 2022 May. Fundam Res. 2021. PMID: 38933404 Free PMC article.
-
Development and challenges of polarization-sensitive photodetectors based on 2D materials.Nanoscale Horiz. 2025 Apr 22;10(5):847-872. doi: 10.1039/d4nh00624k. Nanoscale Horiz. 2025. PMID: 39936216 Review.
-
Van Der Waals Hybrid Integration of 2D Semimetals for Broadband Photodetection.Adv Mater. 2025 Feb 13:e2415717. doi: 10.1002/adma.202415717. Online ahead of print. Adv Mater. 2025. PMID: 39945105 Review.
Cited by
-
Next-Generation Image Sensors Based on Low-Dimensional Semiconductor Materials.Adv Mater. 2025 Jul;37(26):e2501123. doi: 10.1002/adma.202501123. Epub 2025 Apr 16. Adv Mater. 2025. PMID: 40237125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Graphene nanowalls in photodetectors.RSC Adv. 2023 Jul 28;13(33):22838-22862. doi: 10.1039/d3ra03104g. eCollection 2023 Jul 26. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37520101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Nanomaterials for Sensing and Detection.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Jan 4;14(1):128. doi: 10.3390/nano14010128. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38202583 Free PMC article.
-
The application of infrared thermography technology in flap: A perspective from bibliometric and visual analysis.Int Wound J. 2023 Dec;20(10):4308-4327. doi: 10.1111/iwj.14333. Epub 2023 Aug 8. Int Wound J. 2023. PMID: 37551726 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of Low-Dimensional Solid Room-Temperature Photodetectors-Critical View.Materials (Basel). 2024 Sep 14;17(18):4522. doi: 10.3390/ma17184522. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39336263 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rogalski A. History of infrared detectors. Opto-Electron. Rev. 2012;20:279–308. doi: 10.2478/s11772-012-0037-7. - DOI
-
- Ponomarenko V.P., Filachev A.M. Infrared Techniques and Electro-Optics in Russia: A History 1946–2006. Volume 165 SPIE Press; Bellingham, WA, USA: 2007.
-
- Rogalski A., Adamiec K., Rutkowski J. Narrow-Gap Semiconductor Photodiodes. Volume 77 SPIE Press; Bellingham, WA, USA: 2000.
-
- Xiao Y., Zhu H., Deng K., Wang P., Li Q., He T., Zhang T., Miao J., Li N., Lu W. Progress and challenges in blocked impurity band infrared detectors for space-based astronomy. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2022;65:287301. doi: 10.1007/s11433-022-1906-y. - DOI
-
- Wang X., Cui Y., Li T., Lei M., Li J., Wei Z. Recent advances in the functional 2D photonic and optoelectronic devices. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2019;7:1801274. doi: 10.1002/adom.201801274. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

