Rebuildable Silver Nanoparticles Employed as Seeds for Synthesis of Pure Silver Nanopillars with Hexagonal Cross-Sections under Room Temperature
- PMID: 37049356
- PMCID: PMC10097324
- DOI: 10.3390/nano13071263
Rebuildable Silver Nanoparticles Employed as Seeds for Synthesis of Pure Silver Nanopillars with Hexagonal Cross-Sections under Room Temperature
Abstract
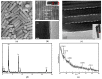
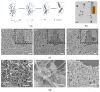
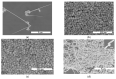
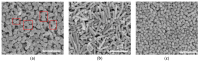
Silver nanopillars with strong plasmonic effects are used for localized electromagnetic field enhancement and regulation and have wide potential applications in sensing, bioimaging, and surface-enhanced spectroscopy. Normally, the controlled synthesis of silver nanopillars is mainly achieved using heterometallic nanoparticles, including Au nanobipyramids and Pd decahedra, as seeds for inducing nanostructure growth. However, the seed materials are usually doped in silver nanopillar products. Herein, the synthesis of pure silver nanopillars with hexagonal cross-sections is achieved by employing rebuildable silver nanoparticles as seeds. An environmentally friendly, stable, and reproducible synthetic route for obtaining silver nanopillars is proposed using sodium dodecyl sulfate as the surface stabilizer. Furthermore, the seed particles induce the formation of regular structures at different temperatures, and, specifically, room temperature is beneficial for the growth of nanopillars. The availability of silver nanoparticle seeds using sodium alginate as a carrier at different temperatures was verified. A reproducible method was developed to synthesize pure silver nanopillars from silver nanoparticles at room temperature, which can provide a strategy for designing plasmonic nanostructures for chemical and biological applications.
Keywords: high repeatability; room temperature; silver nanoparticle seed; silver nanopillar synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synthesis of Silver Nanoplates with the Assistance of Natural Polymer (Sodium Alginate) Under 0 °C.Materials (Basel). 2020 Aug 30;13(17):3827. doi: 10.3390/ma13173827. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32872579 Free PMC article.
-
Design of Magnetic-Plasmonic Nanoparticle Assemblies via Interface Engineering of Plasmonic Shells for Targeted Cancer Cell Imaging and Separation.Small. 2020 May;16(20):e2001103. doi: 10.1002/smll.202001103. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Small. 2020. PMID: 32329574
-
Synthesis and sensing properties of D5h pentagonal silver star nanoparticles.Nanoscale. 2016 Nov 3;8(43):18282-18290. doi: 10.1039/c6nr07397b. Nanoscale. 2016. PMID: 27766337
-
Single nanoparticle plasmonic sensors.Sensors (Basel). 2015 Oct 12;15(10):25774-92. doi: 10.3390/s151025774. Sensors (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26473866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silver-Based Plasmonic Nanoparticles for and Their Use in Biosensing.Biosensors (Basel). 2019 Jun 10;9(2):78. doi: 10.3390/bios9020078. Biosensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31185689 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jiang W., Hu H., Deng Q., Zhang S., Xu H. Temperature-dependent dark-field scattering of single plasmonic nanocavity. Nanophotonics. 2020;9:3347–3356. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2020-0076. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

