Low Zinc Alleviates the Progression of Thoracic Aortic Dissection by Inhibiting Inflammation
- PMID: 37049478
- PMCID: PMC10096567
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15071640
Low Zinc Alleviates the Progression of Thoracic Aortic Dissection by Inhibiting Inflammation
Abstract
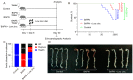
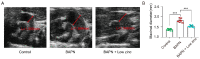
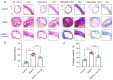
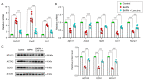
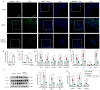
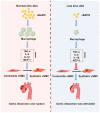
Vascular inflammation triggers the development of thoracic aortic dissection (TAD). Zinc deficiency could dampen tissue inflammation. However, the role of zinc as a nutritional intervention in the progression of TAD remains elusive. In this study, we employed a classical β-aminopropionitrile monofumarate (BAPN)-induced TAD model in mice treated with low zinc and observed that the TAD progression was greatly ameliorated under low zinc conditions. Our results showed that low zinc could significantly improve aortic dissection and rupture (BAPN + low zinc vs. BAPN, 36% vs. 100%) and reduce mortality (BAPN + low zinc vs. BAPN, 22% vs. 57%). Mechanically, low zinc attenuated the infiltration of macrophages and inhibited the expression of inflammatory cytokines, suppressed the phenotype switch of vascular smooth muscle cells from contractile to synthetic types, and eventually alleviated the development of TAD. In conclusion, this study suggested that low zinc may serve as a potential nutritional intervention approach for TAD prevention.
Keywords: inflammation; low zinc; phenotypic transition; thoracic aortic dissection; vascular smooth muscle cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ACE2 deficiency inhibits thoracic aortic dissection by enhancing SIRT3 mediated inhibition of inflammation and VSCMs phenotypic switch.Mol Med. 2024 Sep 19;30(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00926-4. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39300372 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent Hypoxia Alleviates β-Aminopropionitrile Monofumarate Induced Thoracic Aortic Dissection in C57BL/6 Mice.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2020 Jun;59(6):1000-1010. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2019.10.014. Epub 2019 Dec 24. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2020. PMID: 31879145
-
Legumain Is an Endogenous Modulator of Integrin αvβ3 Triggering Vascular Degeneration, Dissection, and Rupture.Circulation. 2022 Mar;145(9):659-674. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.056640. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Circulation. 2022. PMID: 35100526
-
Induction of thoracic aortic dissection: a mini-review of β-aminopropionitrile-related mouse models.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2020 Aug.;21(8):603-610. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2000022. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2020. PMID: 32748576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Latest Findings on the Pathogenic Mechanisms of Thoracic Aortic Dissection].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 May;54(3):699-704. doi: 10.12182/20230260101. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37248608 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
The role of oxidative stress in aortic dissection: a potential therapeutic target.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jul 12;11:1410477. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1410477. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39070552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay of ferroptosis and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of aortic dissection.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 5;16:1519273. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1519273. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39974735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Trace Elements in Cardiovascular Diseases.Toxics. 2023 Nov 23;11(12):956. doi: 10.3390/toxics11120956. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 38133357 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hagan P.G., Nienaber C.A., Isselbacher E.M., Bruckman D., Karavite D.J., Russman P.L., Evangelista A., Fattori R., Suzuki T., Oh J.K., et al. The International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD): New insights into an old disease. JAMA. 2000;283:897–903. doi: 10.1001/jama.283.7.897. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

