Convolvulus pluricaulis Choisy's Extraction, Chemical Characterization and Evaluation of the Potential Effects on Glycaemic Balance in a 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Cell Model
- PMID: 37049568
- PMCID: PMC10097163
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15071727
Convolvulus pluricaulis Choisy's Extraction, Chemical Characterization and Evaluation of the Potential Effects on Glycaemic Balance in a 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Cell Model
Abstract
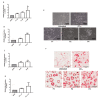
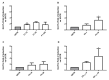
Convolvulus pluricaulis (CP) is a common Indian herb, largely employed in Ayurvedic medicine and known for its neuroprotective and neuroinflammatory action. Its effectiveness against several pathologic/sub-pathologic conditions is widely accepted, but it is not yet completely chemically characterized. In recent years, several researchers have pointed out the involvement of CP and other Convolvulaceae in lipidic and glucidic metabolism, particularly in the control of hyperlipidaemia and diabetic conditions. In this scenario, the aim of the study was to chemically characterize the medium polarity part of the CP whole plant and its fractions and to shed light on their biological activity in adipocyte differentiation using the 3T3-L1 cell model. Our results demonstrated that the CP extract and fractions could upregulate the adipocyte differentiation through the modulation of the nuclear receptor PPARγ (Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ), broadly recognized as a key regulator of adipocyte differentiation, and the glucose transporter GLUT-4, which is fundamental for cellular glucose uptake and for metabolism control. CP also showed the ability to exert an anti-inflammatory effect, downregulating cytokines such as Rantes, MCP-1, KC, eotaxin, and GM-CSF, which are deeply involved in insulin resistance and glucose intolerance. Taken together, these data suggest that CP could exert a potential beneficial effect on glycemia and could be employed as an anti-diabetic adjuvant or, in any case, a means to better control glucose homeostasis.
Keywords: 3T3-L1; Convolvulus pluricaulis Choisy; GLUT-4; PPARγ; adipocyte differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
α, β-Amyrin, a pentacyclic triterpenoid from Protium heptaphyllum suppresses adipocyte differentiation accompanied by down regulation of PPARγ and C/EBPα in 3T3-L1 cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jan;109:1860-1866. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.027. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30551441
-
Artepillin C, as a PPARγ ligand, enhances adipocyte differentiation and glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2011 Apr 1;81(7):925-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.01.002. Epub 2011 Jan 8. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21219874
-
Suppression of adipocyte differentiation and lipid accumulation by stearidonic acid (SDA) in 3T3-L1 cells.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Sep 25;16(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0574-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28946872 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of black soybean koji extract on glucose utilization and adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 May 9;15(5):8280-92. doi: 10.3390/ijms15058280. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24821545 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Shankhpushpi (Convolvulus pluricaulis) in neurological disorders: An umbrella review covering evidence from ethnopharmacology to clinical studies.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022 Sep;140:104795. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104795. Epub 2022 Jul 22. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022. PMID: 35878793
Cited by
-
The Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Merremia umbellata Extract.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Nov 23;12(12):2037. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122037. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136157 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

