Carnosine and Beta-Alanine Supplementation in Human Medicine: Narrative Review and Critical Assessment
- PMID: 37049610
- PMCID: PMC10096773
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15071770
Carnosine and Beta-Alanine Supplementation in Human Medicine: Narrative Review and Critical Assessment
Abstract
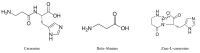
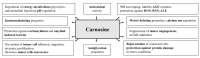
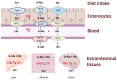
The dipeptide carnosine is a physiologically important molecule in the human body, commonly found in skeletal muscle and brain tissue. Beta-alanine is a limiting precursor of carnosine and is among the most used sports supplements for improving athletic performance. However, carnosine, its metabolite N-acetylcarnosine, and the synthetic derivative zinc-L-carnosine have recently been gaining popularity as supplements in human medicine. These molecules have a wide range of effects-principally with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiglycation, anticarbonylation, calcium-regulatory, immunomodulatory and chelating properties. This review discusses results from recent studies focusing on the impact of this supplementation in several areas of human medicine. We queried PubMed, Web of Science, the National Library of Medicine and the Cochrane Library, employing a search strategy using database-specific keywords. Evidence showed that the supplementation had a beneficial impact in the prevention of sarcopenia, the preservation of cognitive abilities and the improvement of neurodegenerative disorders. Furthermore, the improvement of diabetes mellitus parameters and symptoms of oral mucositis was seen, as well as the regression of esophagitis and taste disorders after chemotherapy, the protection of the gastrointestinal mucosa and the support of Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment. However, in the areas of senile cataracts, cardiovascular disease, schizophrenia and autistic disorders, the results are inconclusive.
Keywords: beta-alanine; carnosine; health benefits; human diseases; supplementation; zinc-carnosine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An "enigmatic" L-carnosine (β-alanyl-L-histidine)? Cell proliferative activity as a fundamental property of a natural dipeptide inherent to traditional antioxidant, anti-aging biological activities: balancing and a hormonally correct agent, novel patented oral therapy dosage formulation for mobility, skeletal muscle power and functional performance, hypothalamic-pituitary- brain relationship in health, aging and stress studies.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2015;9(1):1-64. doi: 10.2174/1872211309666141218145408. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2015. PMID: 25524476 Review.
-
Beta-alanine supplementation, muscle carnosine and exercise performance.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2015 Jan;18(1):63-70. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000127. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2015. PMID: 25474013 Review.
-
[Effects of ß-alanine supplementation on athletic performance].Nutr Hosp. 2014 Oct 6;31(1):155-69. doi: 10.3305/nh.2015.31.1.7517. Nutr Hosp. 2014. PMID: 25561107 Review. Spanish.
-
Effects of Histidine and β-alanine Supplementation on Human Muscle Carnosine Storage.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2017 Mar;49(3):602-609. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000001213. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2017. PMID: 28106620
-
Effect of beta-alanine supplementation on muscle carnosine concentrations and exercise performance.Amino Acids. 2010 Jul;39(2):321-33. doi: 10.1007/s00726-009-0443-4. Epub 2009 Dec 20. Amino Acids. 2010. PMID: 20091069 Review.
Cited by
-
Comment on Cesak et al. Carnosine and Beta-Alanine Supplementation in Human Medicine: Narrative Review and Critical Assessment. Nutrients2023, 15, 1770.Nutrients. 2024 Aug 2;16(15):2522. doi: 10.3390/nu16152522. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39125401 Free PMC article.
-
State of the Art in the Development of Human Serum Carnosinase Inhibitors.Molecules. 2024 May 24;29(11):2488. doi: 10.3390/molecules29112488. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38893364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Carnosine-Niosomal Delivery System for Targeted Cancer Therapy".Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Jun;83(2):1495-1520. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01626-w. Epub 2024 Dec 10. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39656368 Review.
-
Amino acid profile alteration in age-related atrial fibrillation.J Transl Med. 2024 Mar 9;22(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05028-7. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38461346 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-organ multi-omic and gut microbiome markers of fat and sucrose dietary oversupply in cardiometabolic disease.iScience. 2025 Mar 1;28(4):111887. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.111887. eCollection 2025 Apr 18. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40463962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xing L., Chee M.E., Zhang H., Zhang W., Mine Y. Carnosine—A natural bioactive dipeptide: Bioaccessibility, bioavailability and health benefits. J. Food. Bioact. 2019;5:8–17. doi: 10.31665/JFB.2019.5174. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

