Combining Copper and Zinc into a Biosensor for Anti-Chemoresistance and Achieving Osteosarcoma Therapeutic Efficacy
- PMID: 37049685
- PMCID: PMC10096333
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28072920
Combining Copper and Zinc into a Biosensor for Anti-Chemoresistance and Achieving Osteosarcoma Therapeutic Efficacy
Abstract
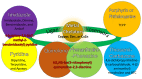
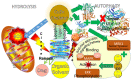
Due to its built-up chemoresistance after prolonged usage, the demand for replacing platinum in metal-based drugs (MBD) is rising. The first MBD approved by the FDA for cancer therapy was cisplatin in 1978. Even after nearly four and a half decades of trials, there has been no significant improvement in osteosarcoma (OS) therapy. In fact, many MBD have been developed, but the chemoresistance problem raised by platinum remains unresolved. This motivates us to elucidate the possibilities of the copper and zinc (CuZn) combination to replace platinum in MBD. Thus, the anti-chemoresistance properties of CuZn and their physiological functions for OS therapy are highlighted. Herein, we summarise their chelators, main organic solvents, and ligand functions in their structures that are involved in anti-chemoresistance properties. Through this review, it is rational to discuss their ligands' roles as biosensors in drug delivery systems. Hereafter, an in-depth understanding of their redox and photoactive function relationships is provided. The disadvantage is that the other functions of biosensors cannot be elaborated on here. As a result, this review is being developed, which is expected to intensify OS drugs with higher cure rates. Nonetheless, this advancement intends to solve the major chemoresistance obstacle towards clinical efficacy.
Keywords: CuZn; Osteosarcoma Therapy; anti-chemoresistance; ligand biosensors; metal-based drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dang W., Wang Y., Chen W.-C., Ju E., Mintz R.L., Teng Y., Zhu L., Wang K., Lv S., Chan H.F., et al. Implantable 3D Printed Hydrogel Scaffolds Loading Copper-Doxorubicin Complexes for Postoperative Chemo/Chemodynamic Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2023;15:4911–4923. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c18494. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang Q., Kuang G., Zhang L., Zhu Y. Nanocarriers for Platinum Drug Delivery. Biomed Technol. 2023;2:77–89. doi: 10.1016/j.bmt.2022.11.011. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

