Discrepancy Study of the Chemical Constituents of Panax Ginseng from Different Growth Environments with UPLC-MS-Based Metabolomics Strategy
- PMID: 37049688
- PMCID: PMC10095802
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28072928
Discrepancy Study of the Chemical Constituents of Panax Ginseng from Different Growth Environments with UPLC-MS-Based Metabolomics Strategy
Abstract
Panax ginseng (P. ginseng), the dried root and rhizome of P. ginseng C. A. Meyer, is widely used in many fields as dietary supplements and medicine. To characterize the chemical constituents in P. ginseng cultivated in different growth environments, a UPLC-TOF-MS method was established for qualitative analysis. Four hundred and eight ginsenosides, including 81 new compounds, were characterized in P. ginseng from different regions. Among the detected compounds, 361 ginsenosides were recognized in P. ginseng cultivated in the region of Monsoon Climate of Medium Latitudes, possessing the largest amount of ginsenosides in all samples. Furthermore, 41 ginsenosides in 12 batches of P. ginsengs were quantified with a UPLC-MRM-MS method, and P. ginsengs from different regions were distinguished via chemometric analysis. This study showed that the different environments have a greater influence on P. ginseng, which laid a foundation for further quality control of the herb.
Keywords: P. ginseng; UPLC-MS/MS; ginsenosides; growth environment; metabolomics; multivariate statistical analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
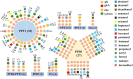
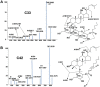
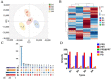
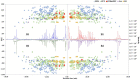
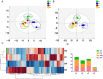
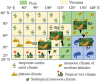
References
-
- Zhou R., He D., Xie J., Zhou Q., Zeng H., Li H., Huang L. The Synergistic Effects of Polysaccharides and Ginsenosides From American Ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) Ameliorating Cyclophosphamide-Induced Intestinal Immune Disorders and Gut Barrier Dysfunctions Based on Microbiome-Metabolomics Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2021;12:665901. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.665901. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

