Catalytic, Theoretical, and Biological Investigations of Ternary Metal (II) Complexes Derived from L-Valine-Based Schiff Bases and Heterocyclic Bases
- PMID: 37049692
- PMCID: PMC10095770
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28072931
Catalytic, Theoretical, and Biological Investigations of Ternary Metal (II) Complexes Derived from L-Valine-Based Schiff Bases and Heterocyclic Bases
Abstract
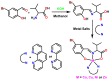
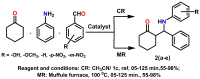
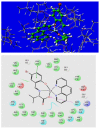
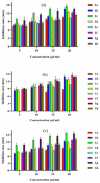
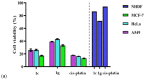
A new series of ternary metal complexes, including Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II), were synthesized and characterized by elemental analysis and diverse spectroscopic methods. The complexes were synthesized from respective metal salts with Schiff's-base-containing amino acids, salicylaldehyde derivatives, and heterocyclic bases. The amino acids containing Schiff bases showed promising pharmacological properties upon complexation. Based on satisfactory elemental analyses and various spectroscopic techniques, these complexes revealed a distorted, square pyramidal geometry around metal ions. The molecular structures of the complexes were optimized by DFT calculations. Quantum calculations were performed with the density functional method for which the LACVP++ basis set was used to find the optimized molecular structure of the complexes. The metal complexes were subjected to an electrochemical investigation to determine the redox behavior and oxidation state of the metal ions. Furthermore, all complexes were utilized for catalytic assets of a multi-component Mannich reaction for the preparation of -amino carbonyl derivatives. The synthesized complexes were tested to determine their antibacterial activity against E. coli, K. pneumoniae, and S. aureus bacteria. To evaluate the cytotoxic effects of the Cu(II) complexes, lung cancer (A549), cervical cancer (HeLa), and breast cancer (MCF-7) cells compared to normal cells, cell lines such as human dermal fibroblasts (HDF) were used. Further, the docking study parameters were supported, for which it was observed that the metal complexes could be effective in anticancer applications.
Keywords: Cu(II) complexes; L-valine; antibacterial activity; binding interaction; ternary metal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Synthesis, spectroscopic and biological activity evaluation of Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) complexes of schiff base derived from pyridoxal and 4-fluorobenzohydrazide.Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2021;40(8):845-866. doi: 10.1080/15257770.2021.1961271. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 34379029
-
New Schiff base ligand and its novel Cr(III), Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), Zn(II) complexes: spectral investigation, biological applications, and semiconducting properties.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 26;12(1):17942. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22713-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36289280 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial study of polymeric transition metal complexes of Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II).Microb Pathog. 2017 Sep;110:414-425. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.07.008. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Microb Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28729223
-
Schiff Bases and their Metal Complexes as Potential Anticancer Candidates: A Review of Recent Works.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019;19(15):1786-1795. doi: 10.2174/1871520619666190227171716. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30827264 Review.
-
Recent advances in Schiff bases and Cu(II) complexes: Applications in fluorescence imaging and anticancer therapy (2020-2024).J Inorg Biochem. 2025 Jul;268:112909. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2025.112909. Epub 2025 Apr 3. J Inorg Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40194476 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemical, Pharmacological, and Theoretical Aspects of Some Transition Metal(II) Complexes Derived from Pyrrole Azine Schiff Base.ACS Omega. 2023 Sep 14;8(38):34458-34470. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c02860. eCollection 2023 Sep 26. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37779929 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosenberg B., VanCamp L. The successful regression of large solid sarcoma 180 tumors by platinum compounds. Cancer Res. 1970;30:1799–1802. - PubMed
-
- Creaven B.S., Duff B., Egan D.A., Kavanagh K., Rosair G., Thangella V.R., Walsh M. Anticancer and antifungal activity of copper (II) complexes of quinolin-2 (1H)-one-derived Schiff bases. Inorg. Chim. Acta. 2010;363:4048–4058. doi: 10.1016/j.ica.2010.08.009. - DOI
-
- Sondhi S.M., Singh N., Kumar A., Lozach O., Meijer L. Synthesis, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and kinase (CDK-1, CDK-5 and GSK-3) inhibition activity evaluation of benzimidazole/benzoxazole derivatives and some Schiff’s bases. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2006;14:3758–3765. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2006.01.054. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

