Cleistocalyx nervosum var. paniala Berry Seed Protects against TNF-α-Stimulated Neuroinflammation by Inducing HO-1 and Suppressing NF-κB Mechanism in BV-2 Microglial Cells
- PMID: 37049819
- PMCID: PMC10095692
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28073057
Cleistocalyx nervosum var. paniala Berry Seed Protects against TNF-α-Stimulated Neuroinflammation by Inducing HO-1 and Suppressing NF-κB Mechanism in BV-2 Microglial Cells
Abstract
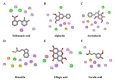
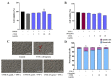
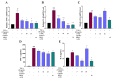
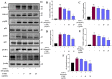
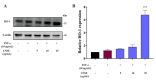
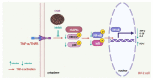
Sustained inflammatory responses have been implicated in various neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs). Cleistocalyx nervosum var. paniala (CN), an indigenous berry, has been reported to exhibit several health-beneficial properties. However, investigation of CN seeds is still limited. The objective of this study was to evaluate the protective effects of ethanolic seed extract (CNSE) and mechanisms in BV-2 mouse microglial cells using an inflammatory stimulus, TNF-α. Using LC-MS, ferulic acid, aurentiacin, brassitin, ellagic acid, and alpinetin were found in CNSE. Firstly, we examined molecular docking to elucidate its bioactive components on inflammation-related mechanisms. The results revealed that alpinetin, aurentiacin, and ellagic acid inhibited the NF-κB activation and iNOS function, while alpinetin and aurentiacin only suppressed the COX-2 function. Our cell-based investigation exhibited that cells pretreated with CNSE (5, 10, and 25 μg/mL) reduced the number of spindle cells, which was highly observed in TNF-α treatment (10 ng/mL). CNSE also obstructed TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 mRNA levels and repressed the TNF-α and IL-6 releases in a culture medium of BV-2 cells. Remarkably, CNSE decreased the phosphorylated forms of ERK, p38MAPK, p65, and IκB-α related to the inhibition of NF-κB binding activity. CNSE obviously induced HO-1 protein expression. Our findings suggest that CNSE offers good potential for preventing inflammatory-related NDDs.
Keywords: Cleistocalyx nervosum var. paniala; MAPKs; NF-κB; TNF-α; microglial cells; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Neuroinflammation Intervention with Medicinal Plants: A Critical and Narrative Review of the Current Literature.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jan 20;18(1):133. doi: 10.3390/ph18010133. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-neuroinflammatory effects of Cleistocalyx nervosum var. paniala berry-seed extract in BV-2 microglial cells via inhibition of MAPKs/NF-κB signaling pathway.Heliyon. 2022 Nov 28;8(11):e11869. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11869. eCollection 2022 Nov. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36468101 Free PMC article.
-
Z-guggulsterone negatively controls microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via blocking IκB-α-NF-κB signals.Neurosci Lett. 2016 Apr 21;619:34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.02.021. Epub 2016 Feb 12. Neurosci Lett. 2016. PMID: 26879835
-
Attenuation of inflammatory-mediated neurotoxicity by Saururus chinensis extract in LPS-induced BV-2 microglia cells via regulation of NF-κB signaling and anti-oxidant properties.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 16;14:502. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-502. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25514974 Free PMC article.
-
Role of TNF-α in the Pathogenesis of Migraine.Pain Res Manag. 2024 Jan 3;2024:1377143. doi: 10.1155/2024/1377143. eCollection 2024. Pain Res Manag. 2024. PMID: 38213956 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Carbon Nanodots Inhibit Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Induced Endothelial Inflammation through Scavenging Hydrogen Peroxide and Upregulating Antioxidant Gene Expression in EA.hy926 Endothelial Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Feb 10;13(2):224. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020224. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397822 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Neuroinflammation Intervention with Medicinal Plants: A Critical and Narrative Review of the Current Literature.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jan 20;18(1):133. doi: 10.3390/ph18010133. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Neuroinflammatory Potential of Areca Nut Extract and Its Bioactive Compounds in Anthracene-Induced BV-2 Microglial Cell Activation.Nutrients. 2024 Aug 28;16(17):2882. doi: 10.3390/nu16172882. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39275198 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

