Biosynthesis of Nanoparticles Using Plant Extracts and Essential Oils
- PMID: 37049821
- PMCID: PMC10095647
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28073060
Biosynthesis of Nanoparticles Using Plant Extracts and Essential Oils
Abstract
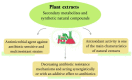
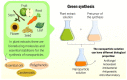
Plant extracts and essential oils have a wide variety of molecules with potential application in different fields such as medicine, the food industry, and cosmetics. Furthermore, these plant derivatives are widely interested in human and animal health, including potent antitumor, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, and bactericidal activity. Given this diversity, different methodologies were needed to optimize the extraction, purification, and characterization of each class of biomolecules. In addition, these plant products can still be used in the synthesis of nanomaterials to reduce the undesirable effects of conventional synthesis routes based on hazardous/toxic chemical reagents and associate the properties of nanomaterials with those present in extracts and essential oils. Vegetable oils and extracts are chemically complex, and although they are already used in the synthesis of nanomaterials, limited studies have examined which molecules are effectively acting in the synthesis and stabilization of these nanostructures. Similarly, few studies have investigated whether the molecules coating the nanomaterials derived from these extracts and essential oils would bring benefits or somehow reduce their potential activity. This synergistic effect presents a promising field to be further explored. Thus, in this review article, we conducted a comprehensive review addressing the main groups of molecules present in plant extracts and essential oils, their extraction capacity, and available methodologies for their characterization. Moreover, we highlighted the potential of these plant products in the synthesis of different metallic nanomaterials and their antimicrobial capacity. Furthermore, we correlated the extract's role in antimicrobial activity, considering the potential synergy between molecules from the plant product and the different metallic forms associated with nanomaterials.
Keywords: antibacterial activity; antioxidant activity; carotenoids; essential oils; green synthesis; nanoparticles; plant extracts; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Essential Oils and Mono/bi/tri-Metallic Nanocomposites as Alternative Sources of Antimicrobial Agents to Combat Multidrug-Resistant Pathogenic Microorganisms: An Overview.Molecules. 2020 Feb 27;25(5):1058. doi: 10.3390/molecules25051058. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32120930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In-vitro assessment of antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of methanol extracts and essential oil of Thymus hirtus sp. algeriensis.Lipids Health Dis. 2014 Jul 14;13:114. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-13-114. Lipids Health Dis. 2014. PMID: 25022197 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of plant terpenoids in the synthesis of colloidal silver nanoparticles.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2016 Aug;234:132-141. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2016.04.008. Epub 2016 May 4. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2016. PMID: 27181393 Review.
-
Plant extract-based synthesis of metallic nanomaterials, their applications, and safety concerns.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2022 Sep;119(9):2273-2304. doi: 10.1002/bit.28148. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2022. PMID: 35635495 Review.
-
Plants-derived bioactives: Novel utilization as antimicrobial, antioxidant and phytoreducing agents for the biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles.Microb Pathog. 2021 Sep;158:105107. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105107. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Microb Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34303810 Review.
Cited by
-
Sustainable Pest Management Using Novel Nanoemulsions of Honeysuckle and Patchouli Essential Oils against the West Nile Virus Vector, Culex pipiens, under Laboratory and Field Conditions.Plants (Basel). 2023 Oct 25;12(21):3682. doi: 10.3390/plants12213682. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37960039 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of Trichoderma harzianum secretome and their role in the biosynthesis of zinc/iron oxide nanoparticles.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 25;15(1):3252. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87581-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39863789 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing essential oils: advanced extraction, sustainability, and nanotechnology for optimal use.Planta. 2025 Aug 3;262(3):71. doi: 10.1007/s00425-025-04788-w. Planta. 2025. PMID: 40754600 Review.
-
Biosynthesized MgONPs using Syzygium cumini seed extract: Characterization, In vitro anti-oxidant and anti-microbial activity.Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2024 Jun 7;43:e00846. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2024.e00846. eCollection 2024 Sep. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2024. PMID: 39034969 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan/Alginate-Based Nanoparticles for Antibacterial Agents Delivery.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 May 30;19:5021-5044. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S469572. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38832335 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Süntar I. Importance of ethnopharmacological studies in drug discovery: Role of medicinal plants. Phytochem. Rev. 2020;19:1199–1209. doi: 10.1007/s11101-019-09629-9. - DOI
-
- Alasmari A. Phytomedicinal Potential Characterization of Medical Plants (Rumex nervosus and Dodonaea viscose) J. Biochem. Technol. 2020;11:113–121.
-
- Horstmanshoff M. Ancient medicine between hope and fear: Medicament, magic and poison in the Roman Empire. Eur. Rev. 1999;7:37–51. doi: 10.1017/S1062798700003720. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

