Potential Therapeutic Value of the STING Inhibitors
- PMID: 37049889
- PMCID: PMC10096477
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28073127
Potential Therapeutic Value of the STING Inhibitors
Abstract
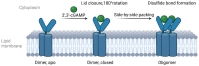
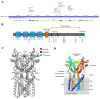
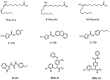
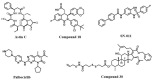
The stimulator of interferon genes (STING) is a critical protein in the activation of the immune system in response to DNA. It can participate the inflammatory response process by modulating the inflammation-preferred translation program through the STING-PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK)-eIF2α pathway or by inducing the secretion of type I interferons (IFNs) and a variety of proinflammatory factors through the recruitment of TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) and interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) or the regulation of the nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) pathway. Based on the structure, location, function, genotype, and regulatory mechanism of STING, this review summarizes the potential value of STING inhibitors in the prevention and treatment of infectious diseases, psoriasis, systemic lupus erythematosus, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and other inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: STING; disease; genotype; inhibitors; innate immunity; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

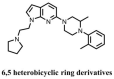
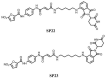
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

