Cell-Free Expression of a Therapeutic Protein Serratiopeptidase
- PMID: 37049893
- PMCID: PMC10095615
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28073132
Cell-Free Expression of a Therapeutic Protein Serratiopeptidase
Abstract
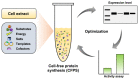
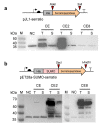
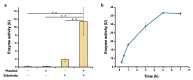
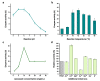
Serratiopeptidase is a clinical therapeutic protein for the treatment of human diseases such as arthritis, bronchitis, and thrombosis. Yet production of this protein in a heterologous host (e.g., Escherichia coli) is difficult due to the issue of protein insolubility and the requirement of laborious refolding procedures. Cell-free protein synthesis (CFPS) systems, derived from crude cell extracts, are effective platforms for the expression of recombinant proteins in vitro. Here, we report a new method to produce serratiopeptidase by using an E. coli-based CFPS system. After rational selection of cell extracts and construction of expression vectors, soluble expression of serratiopeptidase was achieved and the enzyme activity could be readily tested in the cell-free reaction mixture. By further optimizing the key parameters, optimum conditions for the enzyme activity assay were obtained, including the pH value at 5, reaction temperature at 45 °C, substrate concentration at 10 mg/mL, and supplementing Ca2+ ions at 5 mM. Moreover, the CFPS mixture was freeze-dried and the activity of serratiopeptidase could be regenerated by hydration without losing activity. Overall, the CFPS system enabled soluble expression of serratiopeptidase with catalytic activity, providing a new and promising approach for this enzyme production. Our work extends the utility of the cell-free platform to produce therapeutic proteins with clinical applications.
Keywords: cell-free protein synthesis; cell-free synthetic biology; enzymatic activity; serratiopeptidase; therapeutic proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhanced production of recombinant serratiopeptidase in Escherichia coli and its characterization as a potential biosimilar to native biotherapeutic counterpart.Microb Cell Fact. 2019 Dec 17;18(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s12934-019-1267-x. Microb Cell Fact. 2019. PMID: 31847856 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical Preparation of Cell Extract for Cell-Free Protein Synthesis without Physical Disruption.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 29;11(4):e0154614. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154614. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27128597 Free PMC article.
-
Establishing a Klebsiella pneumoniae-Based Cell-Free Protein Synthesis System.Molecules. 2022 Jul 22;27(15):4684. doi: 10.3390/molecules27154684. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35897861 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-Free Systems and Their Importance in the Study of Membrane Proteins.J Membr Biol. 2025 Feb;258(1):15-28. doi: 10.1007/s00232-024-00333-0. Epub 2025 Jan 6. J Membr Biol. 2025. PMID: 39760767 Review.
-
The growing impact of lyophilized cell-free protein expression systems.Bioengineered. 2017 Jul 4;8(4):325-330. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2016.1241925. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Bioengineered. 2017. PMID: 27791452 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Beyond In Vivo, Pharmaceutical Molecule Production in Cell-Free Systems and the Use of Noncanonical Amino Acids Therein.Chem Rev. 2025 Feb 12;125(3):1303-1331. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00126. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Chem Rev. 2025. PMID: 39841856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scale-Up of the Fermentation Process for the Production and Purification of Serratiopeptidase Using Silkworm Pupae as a Substrate.Methods Protoc. 2024 Feb 25;7(2):19. doi: 10.3390/mps7020019. Methods Protoc. 2024. PMID: 38525777 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Hydrogels for Delivery of the Proteolytic Enzyme Serratiopeptidase.Gels. 2024 Feb 20;10(3):156. doi: 10.3390/gels10030156. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38534574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reshma C.V. Microbial enzymes: Therapeutic applications. Microbiol. Res. J. Int. 2019;27:1–8. doi: 10.9734/mrji/2019/v27i230093. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

