Radiolabeled Chalcone Derivatives as Potential Radiotracers for β-Amyloid Plaques Imaging
- PMID: 37049995
- PMCID: PMC10096019
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28073233
Radiolabeled Chalcone Derivatives as Potential Radiotracers for β-Amyloid Plaques Imaging
Abstract
Natural products often provide a pool of pharmacologically relevant precursors for the development of various drug-related molecules. In this review, the research performed on some radiolabeled chalcone derivatives characterized by the presence of the α-β unsaturated carbonyl functional group as potential radiotracers for the imaging of β-amyloids plaques will be summarized. Chalcones' structural modifications and chemical approaches which allow their radiolabeling with the most common SPECT (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography) and PET (Positron Emission Tomography) radionuclides will be described, as well as the state of the art regarding their in vitro binding affinity and in vivo biodistribution and pharmacokinetics in preclinical studies. Moreover, an explanation of the rationale behind their potential utilization as probes for Alzheimer's disease in nuclear medicine applications will be provided.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; chalcones; labeling; radionuclide; α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest and the funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

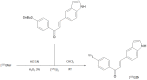

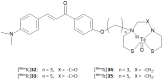
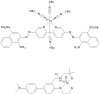
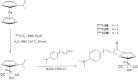
References
-
- Wankhede N.L., Kale M.B., Upaganlawar A.B., Taksande B.G., Umekar M.J., Behl T., Abdellatif A.A.H., Bhaskaran P.M., Dachani S.R., Sehgal A., et al. Involvement of molecular chaperone in protein-misfolding brain diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022;147:112647. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112647. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

