Isolation and Characterization of the Genes Involved in the Berberine Synthesis Pathway in Asian Blue Cohosh, Caulophyllum robustum
- PMID: 37050109
- PMCID: PMC10096549
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12071483
Isolation and Characterization of the Genes Involved in the Berberine Synthesis Pathway in Asian Blue Cohosh, Caulophyllum robustum
Abstract
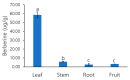
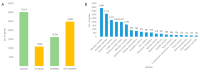
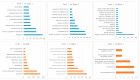
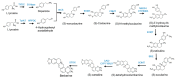
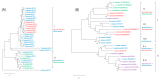
Caulophyllum robustum, commonly named Asian blue cohosh, is a perennial herb in the family Berberidaceae. It has traditionally been used for folk medicine in China. We isolated berberine from the leaves, stem, roots, and fruits of C. robustum, and this is the first report on berberine in this species. Transcriptome analysis was conducted for the characterization of berberine biosynthesis genes in C. robustum, in which, all the genes for berberine biosynthesis were identified. From 40,094 transcripts, using gene ontology (GO) analysis, 26,750 transcripts were assigned their functions in the categories of biological process, molecular function, and cellular component. In the analysis of genes expressed in different tissues, the numbers of genes in the categories of intrinsic component of membrane and transferase activity were up-regulated in leaves versus stem. The berberine synthesis genes in C. robustum were characterized by phylogenetic analysis with corresponding genes from other berberine-producing species. The co-existence of genes from different plant families in the deepest branch subclade implies that the differentiation of berberine synthesis genes occurred early in the evolution of berberine-producing plants. Furthermore, the copy number increment of the berberine synthesis genes was detected at the species level.
Keywords: BIA; Caulophyllum robustum; berberine; blue cohosh; transcriptomes.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have read the manuscript and have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Loconte H., Estes J.R. Generic relationships within Leonticeae (Berberidaceae) Can. J. Bot. 1989;67:2310–2316. doi: 10.1139/b89-295. - DOI
-
- Hutchens A.R. A Handbook of Native American Herbs: The Pocket Guide to 125 Medicinal Plants and Their Uses. Shambhala Publications; Boston, MA, USA: 1992.
-
- Kim Y.-D. Berberidaceae. In: Flora of Korea Editorial Committee, editor. The Genera of Vascular Plants of Korea. Academy Publishing Company; Seoul, Republic of Korea: 2007. pp. 206–209.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

