Phytochemical Profiling, Biological Activities, and In Silico Molecular Docking Studies of Causonis trifolia (L.) Mabb. & J.Wen Shoot
- PMID: 37050122
- PMCID: PMC10097374
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12071495
Phytochemical Profiling, Biological Activities, and In Silico Molecular Docking Studies of Causonis trifolia (L.) Mabb. & J.Wen Shoot
Abstract
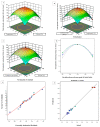
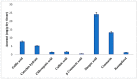
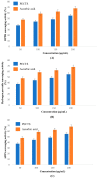
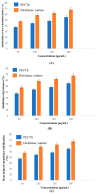
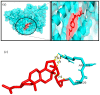
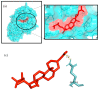
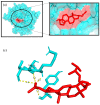
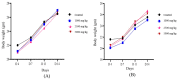
Causonis trifolia (L.) Mabb. & J.Wen, commonly known as "fox grape", is an ethnomedicinally important twining herb of the Vitaceae family, and it is used by ethnic communities for its wide range of therapeutic properties. Our research aims to investigate the chemical composition; antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antidiabetic activities; and mechanisms of interaction between the identified selective chemical compounds and the target proteins associated with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antidiabetic effects of the optimised phenolic extract of Causonis trifolia (L.) Mabb. & J.Wen, shoot (PECTS) to endorse the plant as a potential drug candidate for a future bioprospecting programme. Here, we employed the response surface methodology (RSM) with a Box-Behnken design to enrich the methanolic extract of C. trifolia shoot with phenolic ingredients by optimising three key parameters: solvent concentration (% v/v, methanol:water), extraction temperature (°C), and extraction duration (hours). From the quantitative phytochemical estimation, it was evident that the PECTS contained good amounts of phenolics, flavonoids, tannins, and alkaloids. During the HPLC analysis, we identified a total of eight phenolic and flavonoid compounds (gallic acid, catechin hydrate, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, sinapic acid, coumarin, and kaempferol) and quantified their respective contents from the PECTS. The GC-MS analysis of the PECTS highlighted the presence of 19 phytochemicals. In addition, the bioactivity study of the PECTS showed remarkable potentiality as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antidiabetic agents. In silico molecular docking and computational molecular modelling were employed to investigate the anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antidiabetic properties of the putative bioactive compounds derived from the PECTS using the GC-MS technique to understand the drug-receptor interactions, including their binding pattern. Out of the 19 phytocompounds identified by the GC-MS analysis, one compound, ergosta-5,22-dien-3-ol, acetate, (3β,22E), exhibited the best binding conformations with the target proteins involved in anti-inflammatory (e.g., Tnf-α and Cox-2), antioxidant (SOD), and antidiabetic (e.g., α-amylase and aldo reductase) activities. The nontoxic nature of this optimised extract was also evident during the in vitro cell toxicity assay against the Vero cell line and the in vivo acute toxicity study on BALB/c mice. We believe the results of the present study will pave the way for the invention of novel drugs efficacious for several ailments using the C. trifolia plant.
Keywords: Causonis trifolia; acute toxicity; molecular docking; phytochemical profiling; response surface methodology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
GC-MS analysis of phytoconstituents from Amomum nilgiricum and molecular docking interactions of bioactive serverogenin acetate with target proteins.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 2;10(1):16438. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73442-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33009462 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Characterization, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Cleome arabica L. Fruits Extract against Formalin Induced Chronic Inflammation in Female Wistar Rat: Biochemical, Histological, and In Silico Studies.Molecules. 2022 Dec 21;28(1):26. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010026. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615222 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Composition, Antibacterial, Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Potentials of Cydonia oblonga Bark.Molecules. 2022 Sep 26;27(19):6360. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196360. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36234897 Free PMC article.
-
Ethnomedicinal values of Boerhaavia diffusa L. as a panacea against multiple human ailments: a state of art review.Front Chem. 2023 Nov 14;11:1297300. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1297300. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 38033469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyphenols in Agricultural Grassland Crops and Their Health-Promoting Activities-A Review.Foods. 2023 Nov 14;12(22):4122. doi: 10.3390/foods12224122. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38002180 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Causonis trifolia-based green synthesis of multifunctional silver nanoparticles for dual sensing of mercury and ferric ions, photocatalysis, and biomedical applications.RSC Adv. 2025 May 20;15(21):16879-16893. doi: 10.1039/d5ra01882j. eCollection 2025 May 15. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40395792 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization and Characterization of Phenolic Extraction Conditions and Antioxidant Activity Evaluation of Adenanthera pavonina L. Bark.Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 19;12(22):3902. doi: 10.3390/plants12223902. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38005799 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular docking targeting biofilm and quorum sensing modulation: antimicrobial potential of Salsola tragus.Braz J Microbiol. 2025 Sep;56(3):1805-1821. doi: 10.1007/s42770-025-01689-8. Epub 2025 May 13. Braz J Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40358894
-
Steamed daylily flower (Hemerocallis fulva L.) protected cardiac and hepatic cells against ethanol induced apoptotic and oxidative damage.J Food Drug Anal. 2023 Dec 15;31(4):649-663. doi: 10.38212/2224-6614.3485. J Food Drug Anal. 2023. PMID: 38526821 Free PMC article.
-
LC-MS/MS Profiling, Biological Activities and Molecular Docking Studies of Simmondsia Chinensis Leaves.Chem Biodivers. 2025 Mar;22(3):e202401833. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202401833. Epub 2024 Nov 23. Chem Biodivers. 2025. PMID: 39418480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gupta A.K., Sharma M. Review on Indian Medical Plants. Volume 5. ICMR; New Delhi, India: 2007. pp. 879–882.
-
- Gaur R.D., Sharma J., Painuli R.M. Plants used in traditional healthcare of livestock by Gujjar community of Sub-Himalayan tracts, Uttarakhand, India. Indian J. Nat. Prod. Resour. 2010;1:243–248.
-
- Jasuja N.D. Evaluation of Primary Metabolites and Antioxidant Potential Activity of Cayratia trifolia (Leaf and Stems) J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019;9:367–372. doi: 10.22270/jddt.v9i4-A.3492. - DOI
-
- Khare C.P. Indian Medicinal Plants: An illustrated of Dictionary. Springer; Berlin, Germany: 2007. p. 132.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

