Identification of the NAC Transcription Factor Family during Early Seed Development in Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz
- PMID: 37050144
- PMCID: PMC10096588
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12071518
Identification of the NAC Transcription Factor Family during Early Seed Development in Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz
Abstract
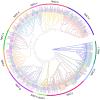
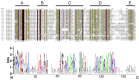
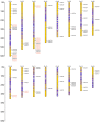
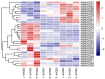
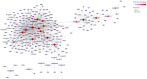
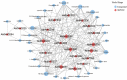
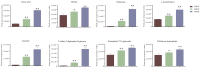
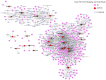
This study aimed to gain an understanding of the possible function of NACs by examining their physicochemical properties, structure, chromosomal location, and expression. Being a family of plant-specific transcription factors, NAC (petunia no apical meristem and Arabidopsis thaliana ATAF1, ATAF2, and CUC2) is involved in plant growth and development. None of the NAC genes has been reported in Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz (A. trifoliata). In this study, we identified 101 NAC proteins (AktNACs) in the A. trifoliata genome by bioinformatic analysis. One hundred one AktNACs were classified into the following twelve categories based on the phylogenetic analysis of NAC protein: NAC-a, NAC-b, NAC-c, NAC-d, NAC-e, NAC-f, NAC-g, NAC-h, NAC-i, NAC-j, NAC-k, and NAC-l. The accuracy of the clustering results was demonstrated based on the gene structure and conserved motif analysis of AktNACs. In addition, we identified 44 pairs of duplication genes, confirming the importance of purifying selection in the evolution of AktNACs. The morphology and microstructure of early A. trifoliata seed development showed that it mainly underwent rapid cell division, seed enlargement, embryo formation and endosperm development. We constructed AktNACs co-expression network and metabolite correlation network based on transcriptomic and metabolomic data of A. trifoliata seeds. The results of the co-expression network showed that 25 AtNAC genes were co-expressed with 233 transcription factors. Metabolite correlation analysis showed that 23 AktNACs were highly correlated with 28 upregulated metabolites. Additionally, 25 AktNACs and 235 transcription factors formed co-expression networks with 141 metabolites, based on correlation analysis involving AktNACs, transcription factors, and metabolites. Notably, AktNAC095 participates in the synthesis of 35 distinct metabolites. Eight of these metabolites, strongly correlated with AktNAC095, were upregulated during early seed development. These studies may provide insight into the evolution, possible function, and expression of AktNACs genes.
Keywords: Akebia trifoliata; NAC family; early seed development; metabolites; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization and expression analysis of the B3 gene family during seed development in Akebia trifoliata.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 9;25(1):1060. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10981-0. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39516780 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis and GC-MS Profiling of Key Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Genes in Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz Seeds.Biology (Basel). 2022 Jun 3;11(6):855. doi: 10.3390/biology11060855. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35741376 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacognostic standardization and machine learning-based investigations on Akebia quinata and Akebia trifoliata.Biomed Chromatogr. 2023 Oct;37(10):e5700. doi: 10.1002/bmc.5700. Epub 2023 Jul 10. Biomed Chromatogr. 2023. PMID: 37429816
-
Akebia quinata and Akebia trifoliata - a review of phytochemical composition, ethnopharmacological approaches and biological studies.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Nov 15;280:114486. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114486. Epub 2021 Aug 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34352331
-
Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz Seed Extract inhibits human hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion in vitro.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Apr 24;234:204-215. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.11.044. Epub 2018 Dec 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30528882
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of the Polygalacturonase Gene Family Sheds Light on the Characteristics, Evolutionary History, and Putative Function of Akebia trifoliata.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 30;24(23):16973. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316973. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069295 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Cloning and Characterization of Transcription Factor FtNAC10 in Tartary Buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum (L.) Gaertn.).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 14;24(22):16317. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216317. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003506 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and expression analysis of the B3 gene family during seed development in Akebia trifoliata.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 9;25(1):1060. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10981-0. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39516780 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the NAC Gene Family and Its Involvement in Cold Response in Dendrobium officinale.Plants (Basel). 2023 Oct 20;12(20):3626. doi: 10.3390/plants12203626. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37896088 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and molecular evolution of NAC gene family in Dendrobium nobile.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Aug 21;14:1232804. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1232804. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37670854 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

