Isolation and Identification of Plant-Growth Inhibitory Constituents from Polygonum chinense Linn and Evaluation of Their Bioherbicidal Potential
- PMID: 37050203
- PMCID: PMC10096564
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12071577
Isolation and Identification of Plant-Growth Inhibitory Constituents from Polygonum chinense Linn and Evaluation of Their Bioherbicidal Potential
Abstract
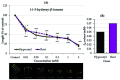
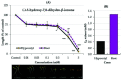
Polygonum chinense Linn. is a medicinal and invasive plant that belongs to the family Polygonaceae. The pharmacological activities and phytochemical constituents of Polygonum chinense are well reported, but the allelopathic effects and potent allelopathic substances of P. chinense remain to be investigated. Hence, this experiment was conducted to separate and characterize potentially allelopathic substances from an extract of the Polygonum chinense plant. The Polygonum chinense plant extracts highly suppressed the growth of cress (Lepidium sativum L.), lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.), barnyard grass (Echinochloa crusgalli (L.) P. Beauv.), and timothy grass (Phleum pratense L.) seedlings in a species- and concentration-dependent way. Two active substances were separated using a series of purification procedures and determined through spectral analysis as (-)-3-hydroxy-β-ionone and (-)-3-hydroxy-7,8-dihydro-β-ionone. These two compounds significantly suppressed the seedling growth of Lepidium sativum (cress) at concentrations of 0.01 and 1 mM, respectively. The extract concentrations necessary for 50% growth inhibition (I50 values) of the cress hypocotyls and roots were 0.05 and 0.07 mM for (-)-3-hydroxy-β-ionone, respectively, and 0.42 and 1.29 mM for (-)-3-hydroxy-7,8-β-ionone, respectively. These findings suggest that these two compounds are in charge of the inhibitory effects of the Polygonum chinense extract and may serve as weed control agents.
Keywords: (−)-3-hydroxy-7,8-β-ionone; (−)-3-hydroxy-β-ionone; Polygonum chinense; allelopathic substances.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


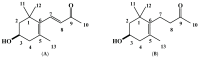
References
-
- Kropff M.J., Walter H. EWRS and the challenges for weed research at the start of a new millennium. Weed Res. 2000;40:7–10. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3180.2000.00166.x. - DOI
-
- Awan T.H., Cruz P.C.S., Chauhan B.S. Agronomic indices, growth, yield-contributing traits, and yield of dry-seeded rice under varying herbicides. Field Crop. Res. 2015;177:5–25. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2015.03.001. - DOI
-
- Molisch H. Der Einfluss Einer Pflanze auf die Andere-Allelopathie. Gustav Fischer Verlag; Jena, Germany: 1937. p. 136.
-
- Rice E.L. Allelopathy. 2nd ed. Academic Press; Orlando, FL, USA: 1984.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

