Electrospun Materials Based on Polymer and Biopolymer Blends-A Review
- PMID: 37050268
- PMCID: PMC10096894
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15071654
Electrospun Materials Based on Polymer and Biopolymer Blends-A Review
Abstract
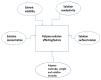
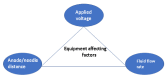
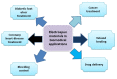
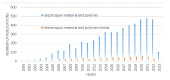
This review covers recent developments and progress in polymer and biopolymer blending and material preparation by electrospinning. Electrospinning is a technique that is used to produce nanofibers to improve the quality of membranes. Electrospun nanofibers are highly applicable in biomedical sciences, supercapacitors, and in water treatment following metal ion adsorption. The key affecting factors of electrospinning have been checked in the literature to obtain optimal conditions of the electrospinning process. Future research directions and outlooks have been suggested to think about innovative ideas for research in this field.
Keywords: biomedical; biopolymer; electrospinning; nanofiber; polymer; supercapacitor; water treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Electrospun nanofibrous membrane for biomedical application.SN Appl Sci. 2022;4(6):172. doi: 10.1007/s42452-022-05056-2. Epub 2022 May 13. SN Appl Sci. 2022. PMID: 35582285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibacterial aroma compounds as property modifiers for electrospun biopolymer nanofibers of proteins and polysaccharides: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Dec 31;253(Pt 2):126563. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126563. Epub 2023 Aug 30. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37657584 Review.
-
Recent Progress and Potential Biomedical Applications of Electrospun Nanofibers in Regeneration of Tissues and Organs.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Apr 7;14(8):1508. doi: 10.3390/polym14081508. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35458258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent update on electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: current trends and their applications.RSC Adv. 2022 Aug 23;12(37):23808-23828. doi: 10.1039/d2ra02864f. eCollection 2022 Aug 22. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36093244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomedical applications of chitosan electrospun nanofibers as a green polymer - Review.Carbohydr Polym. 2019 Mar 1;207:588-600. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.12.011. Epub 2018 Dec 8. Carbohydr Polym. 2019. PMID: 30600043 Review.
Cited by
-
PLA-Based Electrospun Nanofibrous Mats Towards Application as Antibiotic Carriers: Processing Parameters, Fabrication and Characterization.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Apr 30;17(5):589. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17050589. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40430880 Free PMC article.
-
PLA- and PHA-Biopolyester-Based Electrospun Materials: Development, Legislation, and Food Packaging Applications.Molecules. 2024 Nov 19;29(22):5452. doi: 10.3390/molecules29225452. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39598841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smart injectable hydrogels for periodontal regeneration: Recent advancements in biomaterials and biofabrication strategies.Mater Today Bio. 2025 May 11;32:101855. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101855. eCollection 2025 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40487163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Natural Product Extraction Techniques, Electrospun Fiber Fabrication, and the Integration of Experimental Design: A Comprehensive Review.Molecules. 2023 Jul 2;28(13):5163. doi: 10.3390/molecules28135163. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37446825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mucoadhesive nanofibers for ocular drug delivery: mechanisms, design strategies, and applications.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Jun 25. doi: 10.1007/s13346-025-01894-w. Online ahead of print. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40562965
References
-
- Formhals A. Process and Apparatus for Preparing Artificial Threads. 1,975,504. U.S. Patent. 1934 October 2;
-
- Doshi J., Reneker D.H. Electrospinning Process and Applications of Electrospun Fibers; Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 1993 IEEE Industry Applications Conference Twenty-Eighth IAS Annual Meeting; Toronto, ON, Canada. 2–8 October 1993; pp. 1698–1703. - DOI
-
- Wang Z., Crandall C., Sahadevan R., Menkhaus T.J., Fong H. Microfiltration Performance of Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes with Varied Fiber Diameters and Different Membrane Porosities and Thicknesses. Polymer. 2017;114:64–72. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2017.02.084. - DOI
-
- Angammana C.J., Jayaram S.H. Fundamentals of Electrospinning and Processing Technologies. Part. Sci. Technol. 2016;34:72–82. doi: 10.1080/02726351.2015.1043678. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

