Fabrication of Partially Etched Polystyrene Nanoparticles
- PMID: 37050298
- PMCID: PMC10097273
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15071684
Fabrication of Partially Etched Polystyrene Nanoparticles
Abstract
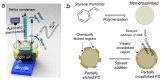
Non-spherical polymer nanoparticles (NPs) have gained attention in various fields, but their fabrication remains challenging. In this study, we present a simple protocol for synthesizing partially etched polystyrene (PS) nanoparticles through emulsion polymerization and chemical etching. By adjusting the degree of crosslinking, we selectively dissolve the weakly crosslinked portions of the particles, resulting in partially etched PS NPs with increased surface area. These partially etched NPs are evaluated for their use as solid surfactants in Pickering emulsions, where they demonstrate significantly improved emulsion stability compared to intact spherical NPs. Our results contribute to the field of nanoparticle shape control and provide insights into developing novel materials for various applications, particularly in the area of solid surfactant usage. Additionally, the importance of conducting cellular toxicity studies using these partially etched NPs for future work is also emphasized.
Keywords: Pickering emulsion; delayed crosslinking; emulsion polymerization; enhanced stability; partially etched nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Wang J., Sun L., Mpoukouvalas K., Lienkamp K., Lieberwirth I., Fassbender B., Bonaccurso E., Brunklaus G., Muehlebach A., Beierlein T. Construction of redispersible polypyrrole core–shell nanoparticles for application in polymer electronics. Adv. Mater. 2009;21:1137–1141. doi: 10.1002/adma.200802787. - DOI
-
- Zhang J., Sun Z., Yang B. Self-assembly of photonic crystals from polymer colloids. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009;14:103–114. doi: 10.1016/j.cocis.2008.09.001. - DOI
-
- Burratti L., De Matteis F., Casalboni M., Francini R., Pizzoferrato R., Prosposito P. Polystyrene photonic crystals as optical sensors for volatile organic compounds. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018;212:274–281. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.03.039. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

