Pressure Drop Dynamics during Filtration of Mixture Aerosol Containing Water, Oil, and Soot Particles on Nonwoven Filters
- PMID: 37050401
- PMCID: PMC10098651
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15071787
Pressure Drop Dynamics during Filtration of Mixture Aerosol Containing Water, Oil, and Soot Particles on Nonwoven Filters
Abstract
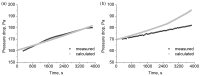
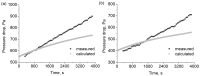
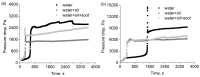
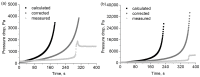
The pressure drop dynamics during the filtration of three-component mixture aerosols are investigated and compared with two and single-component aerosols. The main area of interest is the effect of the addition of a small quantity of liquid (oil) and solid (soot) particles during the filtration of aerosol containing water mist. In addition, calculations of the change in filter mass during oil aerosol filtration have been carried out and compared with the experimental results. The new, improved filtration efficiency model takes into account a better coefficient fitting in the filtration mechanism equations. The limitations in the change in fibre diameter and packing density resulting from the filter loading have been implemented in the model. Additionally, the calculation model employs the fibre size distribution representation via multiple average fibre diameters. The changes in fibre diameter are dependent on each fibre's calculated filtration efficiency. The improved filtration model has been utilised to predict the mass change of the filters during the filtration of pure and mixture aerosols. The pressure drop calculation model based on changes in filter mass has been formulated. The model is then utilised to calculate pressure drop changes resulting from the filtration of the oil aerosol and water and oil mixture aerosol.
Keywords: fibrous filter; filtration efficiency; mixture aerosol; pressure drop; wettability difference.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
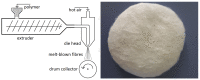
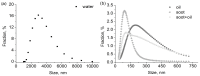
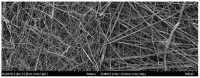
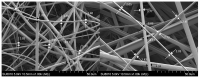
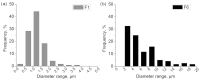
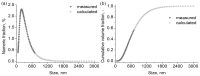
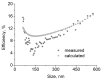
Similar articles
-
Enhanced nano-aerosol loading performance of multilayer PVDF nanofiber electret filters.Sep Purif Technol. 2020 Jun 1;240:116606. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116606. Epub 2020 Jan 25. Sep Purif Technol. 2020. PMID: 32288610 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of pressure drop and filtration efficiency of particulate respirators using welding fumes and sodium chloride.Ann Occup Hyg. 2011 Jul;55(6):666-80. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/mer032. Ann Occup Hyg. 2011. PMID: 21742627
-
Charged PVDF multilayer nanofiber filter in filtering simulated airborne novel coronavirus (COVID-19) using ambient nano-aerosols.Sep Purif Technol. 2020 Aug 15;245:116887. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116887. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Sep Purif Technol. 2020. PMID: 32372877 Free PMC article.
-
Electrostatic charged nanofiber filter for filtering airborne novel coronavirus (COVID-19) and nano-aerosols.Sep Purif Technol. 2020 Nov 1;250:116886. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116886. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Sep Purif Technol. 2020. PMID: 32322159 Free PMC article.
-
Substantial Improvement of Oil Aerosol Filtration Performance Using In-Plane Asymmetric Wettability.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Jun 24;12(25):28852-28860. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c06349. Epub 2020 Jun 9. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 32463655
References
-
- Agranovski I.E., Braddock R.D. Filtration of Liquid Aerosols on Wettable Fibrous Filters. AIChE J. 1998;44:2775–2783. doi: 10.1002/aic.690441218. - DOI
-
- Agranovski I.E., Braddock R.D. Filtration of liquid aerosols on nonwettable fibrous filters. AIChE J. 1998;44:2784–2790. doi: 10.1002/aic.690441219. - DOI
-
- Callé S., Contal P., Thomas D., Bémer D., Leclerc D. Evolutions of efficiency and pressure drop of filter media during clogging and cleaning cycles. Powder Technol. 2002;128:213–217. doi: 10.1016/S0032-5910(02)00199-7. - DOI
-
- Chavhan M.V., Mukhopadhyay A. Fibrous Filter to Protect Building Environments from Polluting Agents: A Review. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. E. 2016;97:63–73. doi: 10.1007/s40034-015-0071-3. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

