Identification, 3D-Reconstruction, and Classification of Dangerous Road Cracks
- PMID: 37050640
- PMCID: PMC10098584
- DOI: 10.3390/s23073578
Identification, 3D-Reconstruction, and Classification of Dangerous Road Cracks
Abstract
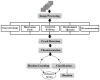
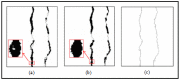
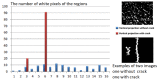
Advances in semiconductor technology and wireless sensor networks have permitted the development of automated inspection at diverse scales (machine, human, infrastructure, environment, etc.). However, automated identification of road cracks is still in its early stages. This is largely owing to the difficulty obtaining pavement photographs and the tiny size of flaws (cracks). The existence of pavement cracks and potholes reduces the value of the infrastructure, thus the severity of the fracture must be estimated. Annually, operators in many nations must audit thousands of kilometers of road to locate this degradation. This procedure is costly, sluggish, and produces fairly subjective results. The goal of this work is to create an efficient automated system for crack identification, extraction, and 3D reconstruction. The creation of crack-free roads is critical to preventing traffic deaths and saving lives. The proposed method consists of five major stages: detection of flaws after processing the input picture with the Gaussian filter, contrast adjustment, and ultimately, threshold-based segmentation. We created a database of road cracks to assess the efficacy of our proposed method. The result obtained are commendable and outperform previous state-of-the-art studies.
Keywords: 3D reconstruction; crack characterization; crack classification; crack detection; image processing; machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





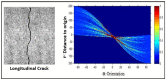









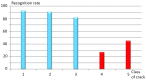
Similar articles
-
Crack Segmentation Extraction and Parameter Calculation of Asphalt Pavement Based on Image Processing.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Nov 14;23(22):9161. doi: 10.3390/s23229161. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38005547 Free PMC article.
-
Three-Stage Pavement Crack Localization and Segmentation Algorithm Based on Digital Image Processing and Deep Learning Techniques.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 3;22(21):8459. doi: 10.3390/s22218459. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36366156 Free PMC article.
-
Pavement Cracks Segmentation Algorithm Based on Conditional Generative Adversarial Network.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 3;22(21):8478. doi: 10.3390/s22218478. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36366176 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Vision-Based Pothole Detection Methods Using Computer Vision and Machine Learning.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Aug 30;24(17):5652. doi: 10.3390/s24175652. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39275561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Exploration of Recent Intelligent Image Analysis Techniques for Visual Pavement Surface Condition Assessment.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 21;22(22):9019. doi: 10.3390/s22229019. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36433612 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bridging Convolutional Neural Networks and Transformers for Efficient Crack Detection in Concrete Building Structures.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jun 30;24(13):4257. doi: 10.3390/s24134257. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001034 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UN Road Safety Fund [(accessed on 21 December 2022)]. Available online: https://unece.org/about-un-road-safety-funds.
-
- Elvik R., Høye A., Vaa T., Sørensen M. The Handbook of Road Safety Measures. 2nd ed. Emerald; Bingley, UK: 2014.
-
- Al-Tit A.A., Dhaou I.B., Albejaidi F.M., Alshitawi M.S. Traffic Safety Factors in the Qassim Region of Saudi Arabia. SAGE Open. 2020;10:2158244020919500. doi: 10.1177/2158244020919500. - DOI
-
- Mannering F.L., Washburn S.S. Principles of Highway Engineering and Traffic Analysis. Wiley; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2020.
-
- Sambito M., Severino A., Freni G., Neduzha L. A systematic review of the hydrological, environmental and durability performance of permeable pavement systems. Sustainability. 2021;13:4509. doi: 10.3390/su13084509. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

