An implementation of the Martini coarse-grained force field in OpenMM
- PMID: 37050876
- PMCID: PMC10398343
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2023.04.007
An implementation of the Martini coarse-grained force field in OpenMM
Abstract
We describe a complete implementation of Martini 2 and Martini 3 in the OpenMM molecular dynamics software package. Martini is a widely used coarse-grained force field with applications in biomolecular simulation, materials, and broader areas of chemistry. It is implemented as a force field but makes extensive use of facilities unique to the GROMACS software, including virtual sites and bonded terms that are not commonly used in standard atomistic force fields. OpenMM is a flexible molecular dynamics package widely used for methods development and is competitive in speed on GPUs with other commonly used packages. OpenMM has facilities to easily implement new force field terms, external forces and fields, and other nonstandard features, which we use to implement all force field terms used in Martini 2 and Martini 3. This allows Martini simulations, starting with GROMACS topology files that are processed by custom scripts, with all the added flexibility of OpenMM. We provide a GitHub repository with test cases, compare accuracy and performance between GROMACS and OpenMM, and discuss the limitations of our implementation in terms of direct comparison with GROMACS. We describe a use case that implements the Modeling Employing Limited Data method to apply experimental constraints in a Martini simulation to efficiently determine the structure of a protein complex. We also discuss issues and a potential solution with the Martini 2 topology for cholesterol.
Copyright © 2023 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
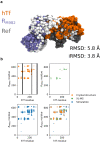
References
-
- Marrink S.J., Monticelli L., et al. Souza P.C.T. Two decades of Martini: better beads, broader scope. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2022;13:e1620. doi: 10.1002/wcms.1620. - DOI
-
- Marrink S.J., de Vries A.H., Mark A.E. Coarse grained model for semiquantitative lipid simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2004;108:750–760. doi: 10.1021/jp036508g. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

