Acetaminophen-induced liver injury: Molecular mechanism and treatments from natural products
- PMID: 37050900
- PMCID: PMC10083499
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1122632
Acetaminophen-induced liver injury: Molecular mechanism and treatments from natural products
Abstract
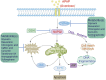
Acetaminophen (APAP) is a widely used analgesic and antipyretic over-the-counter medicine worldwide. Hepatotoxicity caused by APAP overdose is one of the leading causes of acute liver failure (ALF) in the US and in some parts of Europe, limiting its clinical application. Excessive APAP metabolism depletes glutathione and increases N-acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimide (NAPQI) levels, leading to oxidative stress, DNA damage, and cell necrosis in the liver, which in turn leads to liver damage. Studies have shown that natural products such as polyphenols, terpenes, anthraquinones, and sulforaphane can activate the hepatocyte antioxidant defense system with Nrf2 as the core player, reduce oxidative stress damage, and protect the liver. As the key enzyme metabolizing APAP into NAPQI, cytochrome P450 enzymes are also considered to be intriguing target for the treatment of APAP-induced liver injury. Here, we systematically review the hepatoprotective activity and molecular mechanisms of the natural products that are found to counteract the hepatotoxicity caused by APAP, providing reference information for future preclinical and clinical trials of such natural products.
Keywords: Nrf2; acetaminophen; liver injury; natural products; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2023 Liao, Lu, Li, Li, Zhao and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdullah A., Phern T. C., Rahim N. F. H. M., Zaharuddin N. I., Salihin N. M., Yusof A. H., et al. (2017). The effects of cosmos caudatus (ulam Raja) on the levels of expression of Nrf2 target genes in mice liver. J. Pharm. Nutr. Sci. 7, 147–157. 10.6000/1927-5951.2017.07.04.1 - DOI
-
- Agrawal S., Khazaeni B. (2022). Acetaminophen toxicity. St. Petersburg, Florida: StatPearls Publishing. Statpearls [internet] . - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials