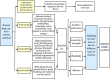
PROTOCOL: Examining the best time of day for exercise: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
- PMID: 37051170
- PMCID: PMC8356310
- DOI: 10.1002/cl2.1144
PROTOCOL: Examining the best time of day for exercise: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Figures
References
-
- Bailey, S. L. , & Heitkemper, M. M. (2001). Circadlan rhythmicity of cortisol and body temperature: Morniningness eveningness effects. Chronobiology International, 18(2), 249–261. - PubMed
-
- Borenstein, M. , Hedges, L. V. , Higgins, J. P. T. , & Rothstein, H. R. (2021). Introduction to meta‐analysis. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons.
-
- Brito, L. C. , Peçanha, T. , Fecchio, R. Y. , Rezende, R. A. , Sousa, P. , DA Silva‐Júnior, N. , Abreu, A. , Silva, G. , Mion‐Junior, D. , Halliwill, J. R. , & Forjaz, C. (2018). Morning versus evening aerobic training effects on blood pressure in treated hypertension. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 51(4), 653–662. 10.1249/MSS.0000000000001852 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources