eEF1A2 siRNA Suppresses MPP+-Induced Activation of Akt and mTOR and Potentiates Caspase-3 Activation in a Parkinson's Disease Model
- PMID: 37051183
- PMCID: PMC10085650
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/1335201
eEF1A2 siRNA Suppresses MPP+-Induced Activation of Akt and mTOR and Potentiates Caspase-3 Activation in a Parkinson's Disease Model
Abstract
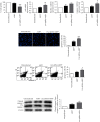
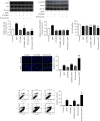
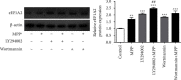
The tissue-specific protein eEF1A2 has been linked to the development of neurological disorders. The role of eEF1A2 in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD) has yet to be investigated. The aim of this study was to determine the potential neuroprotective effects of eEF1A2 in an MPP+ model of PD. Differentiated SH-SY5Y cells were transfected with eEF1A2 siRNA, followed by MPP+ exposure. The expression of p-Akt1 and p-mTORC1 was determined using Western blotting. The expression of p53, Bax, Bcl-2, and caspase-3 was evaluated using qRT-PCR. Cleaved caspase-3 levels and Annexin V/propidium iodide flow cytometry were used to determine apoptosis. The effects of PI3K inhibition were examined. The results showed that eEF1A2 siRNA significantly reduced the eEF1A2 expression induced by MPP+. MPP+ treatment activated Akt1 and mTORC1; however, eEF1A2 knockdown suppressed this activation. In eEF1A2-knockdown cells, MPP+ treatment increased the expression of p53 and caspase-3 mRNA levels as well as increased apoptotic cell death when compared to MPP+ treatment alone. In cells exposed to MPP+, upstream inhibition of the Akt/mTOR pathway, by either LY294002 or wortmannin, inhibited the phosphorylation of Akt1 and mTORC1. Both PI3K inhibitors increased eEF1A2 expression in cells, whether or not they were also treated with MPP+. In conclusion, eEF1A2 may function as a neuroprotective factor against MPP+, in part by regulating the Akt/mTOR pathway upstream.
Copyright © 2023 Kawinthra Khwanraj et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Chambers D. M., Peters J., Abbott C. M. The lethal mutation of the mouse wasted (wst) is a deletion that abolishes expression of a tissue-specific isoform of translation elongation factor 1α, encoded by the Eef1a2 gene. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the U S A . 1998;95(8):4463–4468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.8.4463. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

