How to maximize the therapeutic effect of exosomes on skin wounds in diabetes mellitus: Review and discussion
- PMID: 37051206
- PMCID: PMC10083381
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1146991
How to maximize the therapeutic effect of exosomes on skin wounds in diabetes mellitus: Review and discussion
Abstract
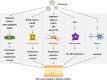
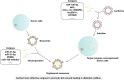
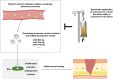
Chronic skin wound healing, especially in diabetes mellitus, is still unsolved. Although many efforts have been made to treat diabetic skin wounds, current strategies have achieved limited effectiveness. Nowadays, a great number of studies have shown that exosomes might be a promising approach for treating diabetic wounds. Many studies and reviews have focused on investigating and discussing the effectiveness and mechanism of exosomes. However, maximizing its value in treating skin wounds in diabetes mellitus requires further consideration. In this review, we reviewed and discussed the aspects that could be further improved in this process, including finding a better source of exosomes, engineering exosomes, adjusting dosage and frequency, and combining more efficient delivery methods. This review provided an overview and idea of what we can do to improve the therapeutic effect of exosomes on skin wounds in diabetes mellitus. Only by combining all the factors that affect the effectiveness of exosomes in diabetic wound healing can we further promote their clinical usefulness.
Keywords: diabetes; exosomes; maximize; skin wounds; therapeutic effect.
Copyright © 2023 Dong, Wu and Tian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Combined Pluronic F127 Hydrogel Promote Chronic Diabetic Wound Healing and Complete Skin Regeneration.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Aug 11;15:5911-5926. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S249129. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32848396 Free PMC article.
-
[Research advances on the role of microRNA engineered exosomes in diabetic wounds].Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2024 Feb 20;40(2):190-195. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501225-20230721-00011. Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38418181 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Mechanism and application of exosomes in the wound healing process in diabetes mellitus.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022 May;187:109882. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2022.109882. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022. PMID: 35487341 Review.
-
Exosomal DMBT1 from human urine-derived stem cells facilitates diabetic wound repair by promoting angiogenesis.Theranostics. 2018 Feb 7;8(6):1607-1623. doi: 10.7150/thno.22958. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29556344 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes derived from pioglitazone-pretreated MSCs accelerate diabetic wound healing through enhancing angiogenesis.J Nanobiotechnology. 2021 May 21;19(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-00894-5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34020670 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Innovative Strategies: Use of Stromal Cell-Derived Secretome for Chronic Wound Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 11;26(12):5609. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125609. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apoptotic Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Promote Skin Repair by Enhancing Angiogenesis: From Death to Regeneration.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jan 16;19:415-428. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S441453. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38250193 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of Apoptotic Extracellular Vesicles from Adipose Tissue and Their Efficacy in Promoting High-Quality Skin Wound Healing.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Jun 2;18:2923-2938. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S411819. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37288352 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes in skin photoaging: biological functions and therapeutic opportunity.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jan 12;22(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01451-3. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38217034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in engineered exosomes for wound repair: current research and future perspectives.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Nov 14;11:1301362. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1301362. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38033824 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Théry C, Witwer K, Aikawa E, Alcaraz M, Anderson J, Andriantsitohaina R, et al. . Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the international society for extracellular vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles (2018) 7(1):1535750. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

