Role of NLRP3 in the pathogenesis and treatment of gout arthritis
- PMID: 37051231
- PMCID: PMC10083392
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1137822
Role of NLRP3 in the pathogenesis and treatment of gout arthritis
Abstract
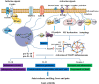
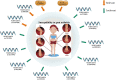
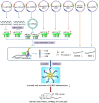
Gout arthritis (GA) is a common and curable type of inflammatory arthritis that has been attributed to a combination of genetic, environmental and metabolic factors. Chronic deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals in articular and periarticular spaces as well as subsequent activation of innate immune system in the condition of persistent hyperuricemia are the core mechanisms of GA. As is well known, drugs for GA therapy primarily consists of rapidly acting anti-inflammatory agents and life-long uric acid lowering agents, and their therapeutic outcomes are far from satisfactory. Although MSU crystals in articular cartilage detected by arthrosonography or in synovial fluid found by polarization microscopy are conclusive proofs for GA, the exact molecular mechanism of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the course of GA still remains mysterious, severely restricting the early diagnosis and therapy of GA. On the one hand, the activation of Nod-like receptor family, pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome requires nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB)-dependent transcriptional enhancement of NLRP3, precursor (pro)-caspase-1 and pro-IL-1β, as well as the assembly of NLRP3 inflammasome complex and sustained release of inflammatory mediators and cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-18 and caspase-1. On the other hand, NLRP3 inflammasome activated by MSU crystals is particularly relevant to the initiation and progression of GA, and thus may represent a prospective diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target. As a result, pharmacological inhibition of the assembly and activation of NLRP3 inflammasome may also be a promising avenue for GA therapy. Herein, we first introduced the functional role of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and relevant biological mechanisms in GA based on currently available evidence. Then, we systematically reviewed therapeutic strategies for targeting NLRP3 by potentially effective agents such as natural products, novel compounds and noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) in the treatment of MSU-induced GA mouse models. In conclusion, our present review may have significant implications for the pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapy of GA.
Keywords: NLRP3; gout arthritis; natural products; ncRNAs; novel compounds; pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Wang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pentagalloyl glucose inhibits monosodium urate-induced inflammation and NLRP3 inflammasome formation via TAK1.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025 Aug 1;329(2):C500-C512. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00673.2024. Epub 2025 Jul 2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40602758 Free PMC article.
-
Rutaecarpine Attenuates Monosodium Urate Crystal-Induced Gouty Inflammation via Inhibition of TNFR-MAPK/NF-κB and NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling Pathways.Chin J Integr Med. 2025 Jul;31(7):590-599. doi: 10.1007/s11655-025-4204-3. Epub 2025 May 8. Chin J Integr Med. 2025. PMID: 40338445
-
Hypocrellin A from an ethnic medicinal fungus protects against NLRP3-driven gout in mice by suppressing inflammasome activation.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 Apr;46(4):1016-1029. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01434-1. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 39681599
-
[Research progress on natural small molecule compound inhibitors of NLRP3 inflammasome].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025 Feb;50(3):644-657. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240828.701. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40350841 Review. Chinese.
-
Natural and synthetic potential drug leads for rheumatoid arthritis probing innovative target: mitochondrial dysfunction and NLRP3 inflammasome activation.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):8295-8312. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03897-3. Epub 2025 Feb 28. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40019529 Review.
Cited by
-
Endovascular Interventional Procedure is a Significant Risk Factor of Postsurgical Gout: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Rheumatol Ther. 2024 Feb;11(1):51-60. doi: 10.1007/s40744-023-00617-2. Epub 2023 Nov 6. Rheumatol Ther. 2024. PMID: 37930614 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of flavonoids in the treatment of gouty arthritis (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2024 Aug;30(2):132. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13256. Epub 2024 May 31. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 38818832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elucidating the molecular landscape of tendinitis: the role of inflammasome-related genes and immune interactions.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 11;15:1393851. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1393851. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38919626 Free PMC article.
-
Research hotspots and trends related to pain in gouty arthritis from 2014 to 2024: A bibliometric analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 15;103(46):e40525. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040525. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39560537 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-hyperuricemia potential of bioactive natural products and extracts derived from traditional Chinese medicines: A review and perspective.J Pharm Anal. 2025 Jul;15(7):101183. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101183. Epub 2025 Jan 3. J Pharm Anal. 2025. PMID: 40708571 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rivera-Paredez B, Macías-Kauffer L, Fernandez-Lopez JC, Villalobos-Comparán M, Martinez-Aguilar MM, de la Cruz-Montoya A, et al. . Influence of genetic and non-genetic risk factors for serum uric acid levels and hyperuricemia in mexicans. Nutrients. (2019) 11(6):1336. doi: 10.3390/nu11061336 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

