Living in a box: Understanding acoustic parameters in the NICU environment
- PMID: 37051427
- PMCID: PMC10083238
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2023.1147226
Living in a box: Understanding acoustic parameters in the NICU environment
Abstract
Background: In the last years, a significant body of scientific literature was dedicated to the noisy environment preterm-born infants experience during their admission to Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICUs). Nonetheless, specific data on sound characteristics within and outside the incubator are missing. Therefore, this study aimed to shed light on noise level and sound characteristics within the incubator, considering the following domain: environmental noise, incubator handling, and respiratory support.
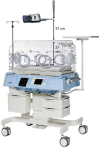
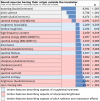
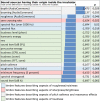
Methods: The study was performed at the Pediatric Simulation Center at the Medical University of Vienna. Evaluation of noise levels inside and outside the incubator was performed using current signal analysis libraries and toolboxes, and differences between dBA and dBSPL values for the same acoustic noises were investigated. Noise level results were furthermore classed within previously reported sound levels derived from a literature survey. In addition, sound characteristics were evaluated by means of more than 70 temporal, spectral, and modulatory timbre features.
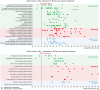
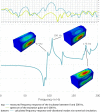
Results: Our results show high noise levels related to various real-life situations within the NICU environment. Differences have been observed between A weighted (dBA) and unweighted (dBSPL) values for the same acoustic stimulus. Sonically, the incubator showed a dampening effect on sounds (less high frequency components, less brightness/sharpness, less roughness, and noisiness). However, a strong tonal booming component was noticeable, caused by the resonance inside the incubator cavity. Measurements and a numerical model identified a resonance of the incubator at 97 Hz and a reinforcement of the sound components in this range of up to 28 dB.
Conclusion: Sound characteristics, the strong low-frequency incubator resonance, and levels in dBSPL should be at the forefront of both the development and promotion of incubators when helping to preserve the hearing of premature infants.
Keywords: NICU; acoustic features; dB (A-weighted vs. unweighted); incubator; noise; preterm; resonance; sound level.
© 2023 Reuter, Bartha-Doering, Czedik-Eysenberg, Maeder, Bertsch, Bibl, Deindl, Berger and Giordano.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

