Predictive value of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in children with acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37051429
- PMCID: PMC10083323
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2023.1147033
Predictive value of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in children with acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Neutrophil gelatin lipase carrier protein (NGAL) has been used as an early biomarker to predict acute kidney injury (AKI). However, the predictive value of NGAL in urine and blood in children with acute kidney injury in different backgrounds remains unclear. Therefore, we conducted this systematic review and meta-analysis to explore the clinical value of NGAL in predicting AKI in children.
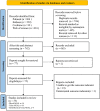
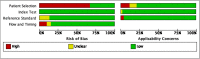
Methods: Computerized databases were searched for relevant the studies published through August 4th, 2022, which included PUBMED, EMBASE, COCHRANE and Web of science. The risk of bias of the original included studies was assessed by using the Quality Assessment of Studies for Diagnostic Accuracy (QUADA-2). At the same time, subgroup analysis of these data was carried out.
Results: Fifty-three studies were included in this meta-analysis, involving 5,049 patients, 1,861 of whom were AKI patients. The sensitivity and specificity of blood NGAL for predicting AKI were 0.79 (95% CI: 0.69-0.86) and 0.85 (95% CI: 0.75-0.91), respectively, and SROC was 0.89 (95% CI: 0.86-0.91). The sensitivity and specificity of urine NGAL for predicting AKI were 0.83 (95% CI: 0.78-0.87) and 0.81 (95% CI: 0.77-0.85), respectively, and SROC was 0.89 (95% CI: 0.86-0.91). Meanwhile, the sensitivity and specificity of overall NGAL (urine and blood NGAL) for predicting AKI in children were 0.82 (95% CI: 0.77-0.86) and 0.82 (95% CI: 0.78-0.86), respectively, and SROC was 0.89 (95% CI: 0.86-0.91).
Conclusion: NGAL is a valuable predictor for AKI in children under different backgrounds. There is no significant difference in the prediction accuracy between urine NGAL and blood NGAL, and there is also no significant difference in different measurement methods of NGAL. Hence, NGAL is a non-invasive option in clinical practice. Based on the current evidence, the accuracy of NGAL measurement is the best at 2 h after cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) and 24 h after birth in asphyxiated newborns.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier: CRD42022360157.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; children; meta-analysis; neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; predictive value.
© 2023 Zou, Chen, Tang, Li and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Measured on Clinical Laboratory Platforms for the Prediction of Acute Kidney Injury and the Associated Need for Dialysis Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Am J Kidney Dis. 2020 Dec;76(6):826-841.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.05.015. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020. PMID: 32679151 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as predictor of acute kidney injury requiring renal replacement therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 21;9:859318. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.859318. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36213627 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and prognosis of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for acute kidney injury with sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Crit Care. 2016 Feb 16;20:41. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1212-x. Crit Care. 2016. PMID: 26880194 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for early diagnosis of cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury: a meta-analysis.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2016 Mar;49(3):746-55. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezv199. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2016. PMID: 26094017 Review.
-
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for predicting acute kidney injury in orthotopic liver transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Jun 1;37(6):683-690. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000002935. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 39976006
Cited by
-
Kidney point-of-care ultrasonography in the PICU: it is about time!Pediatr Nephrol. 2024 Dec;39(12):3379-3382. doi: 10.1007/s00467-024-06407-4. Epub 2024 May 21. Pediatr Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38771323 No abstract available.
-
Assessment of Urinary and Serum Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) Levels as Novel Predictors for Vesicoureteral Reflux Diagnosis in Children with Febrile Urinary Tract Infection.Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2024 May 27;38:59. doi: 10.47176/mjiri.38.59. eCollection 2024. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2024. PMID: 39399612 Free PMC article.
-
KIM-1, IL-18, and NGAL, in the Machine Learning Prediction of Kidney Injury among Children Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation-A Pilot Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 31;24(21):15791. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115791. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958774 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (uNGAL) Reference Intervals in Healthy Adult and Pediatric Individuals Using a Particle-Enhanced Turbidimetric Immunoassay.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jan 3;15(1):95. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15010095. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39795623 Free PMC article.
-
Changing Face of Inflammatory Activation in Complex Coronary Artery Disease during the COVID-19 Pandemic.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 Apr 30;10(5):199. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10050199. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 37233166 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

