Tertiary Syphilitic Gumma Mimicking Testicular Neoplasms
- PMID: 37051441
- PMCID: PMC10085538
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.37392
Tertiary Syphilitic Gumma Mimicking Testicular Neoplasms
Abstract
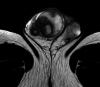
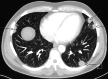
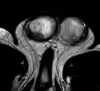
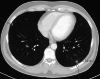
Palpable testicular masses in men aged 20 to 50 years usually represent testicular germ cell tumors. Diagnostic work-up involves ultrasound examination as well as serum tumor markers alpha fetoprotein, beta-human chorionic gonadotropin and lactate dehydrogenase, and particularly the novel marker M371. Orchidectomy is mandatory for germ cell tumors. We report the rare case of testicular involvement by tertiary syphilis mimicking testicular neoplasms with testis-sparing management. A 46-year-old Caucasian male presented with a painless firm mass in the right testicle and multiple cutaneous plaques at the skin of the scrotum, penis and right forearm. Testicular serum tumor markers were negative. Syphilis Rapid Plasma Reagin test and Treponema pallidum immunoglobulin antibodies tests were positive. Radiological examination revealed bilateral testicular lesions as well as bipulmonal pleural-based opacities. Conservative management was attempted and treatment with ceftriaxone (2 g/day) intravenously for 14 days was administered. The testicular findings improved rapidly and significantly during antibiotic treatment. Radiological follow-up examinations after two weeks and two months showed further regression of the testicular and pulmonary lesions. This case represents an extremely rare testicular manifestation of tertiary syphilis. Due to rising syphilis incidence in Europe, tertiary syphilis with formation of gumma should be a differential diagnosis of testicular tumor. Thus, syphilis-specific treatment is safe and orchidectomy can be avoided.
Keywords: bilateral testicular masses; germ-cell tumor; gumma; orchidectomy; tertiary syphilis; testis-sparing management; treponema pallidum.
Copyright © 2023, Angerer et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Management of germ cell tumours of the testis in adult patients. German clinical practice guideline part I: epidemiology, classification, diagnosis, prognosis, fertility preservation, and treatment recommendations for localized stages. Kliesch S, Schmidt S, Wilborn D, et al. Urol Int. 2021;105:169–180. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bilateral calcified testicular gumma. London MZ. J Urol. 1947;57:564–566. - PubMed
-
- Gumma of the testis. Persaud V, Rao A. Br J Urol. 1977;49:142. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
