Platelet-albumin-bilirubin score and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predict intensive care unit admission in patients with end-stage kidney disease infected with the Omicron variant of COVID-19: a single-center prospective cohort study
- PMID: 37051667
- PMCID: PMC10114985
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2199097
Platelet-albumin-bilirubin score and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predict intensive care unit admission in patients with end-stage kidney disease infected with the Omicron variant of COVID-19: a single-center prospective cohort study
Abstract
Objectives: The objective of this study was to develop clinical scores to predict the risk of intensive care unit (ICU) admission in patients with COVID-19 and end stage kidney disease (ESKD).
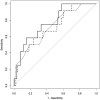
Methods: This was a prospective study in which 100 patients with ESKD were enrolled and divided into two groups: the ICU group and the non-ICU group. We utilized univariate logistic regression and nonparametric statistics to analyze the clinical characteristics and liver function changes of both groups. By plotting receiver operating characteristic curves, we identified clinical scores that could predict the risk of ICU admission.
Results: Out of the 100 patients with Omicron infection, 12 patients were transferred to the ICU due to disease aggravation, with an average of 9.08 days from hospitalization to ICU transfer. Patients transferred to the ICU more commonly experienced shortness of breath, orthopnea, and gastrointestinal bleeding. The peak liver function and changes from baseline in the ICU group were significantly higher, with p values <.05. We found that the baseline platelet-albumin-bilirubin score (PALBI) and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) were good predictors of ICU admission risk, with area under curve values of 0.713 and 0.770, respectively. These scores were comparable to the classic Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE-II) score (p > .05).
Conclusion: Patients with ESKD and Omicron infection who are transferred to the ICU are more likely to have abnormal liver function. The baseline PALBI and NLR scores can better predict the risk of clinical deterioration and early transfer to the ICU for treatment.
Keywords: ICU; Omicron infection; abnormal liver function; end stage kidney disease; inflammation; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; platelet-albumin-bilirubin score.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- https://covid19.who.int/. WHO website. 2022.
-
- Christensen PA, Olsen RJ, Long SW, et al. Signals of significantly increased vaccine breakthrough, decreased hospitalization rates, and less severe disease in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 caused by the omicron variant of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in Houston, Texas. Am J Pathol. 2022;192(4):642–652. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
