Residual coronary artery tree description and lesion EvaluaTion (CatLet) score, clinical variables, and their associations with outcome predictions in patients with acute myocardial infarction
- PMID: 37052135
- PMCID: PMC10586838
- DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002640
Residual coronary artery tree description and lesion EvaluaTion (CatLet) score, clinical variables, and their associations with outcome predictions in patients with acute myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: We have recently developed a new Coronary Artery Tree description and Lesion EvaluaTion (CatLet) angiographic scoring system. Our preliminary studies have demonstrated its superiority over the the Synergy between percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with Taxus and Cardiac Surgery (SYNTAX) score with respect to outcome predictions for acute myocardial infarction (AMI) patients. The current study hypothesized that the residual CatLet (rCatLet) score predicts clinical outcomes for AMI patients and that a combination with the three clinical variables (CVs)-age, creatinine, and ejection fraction, will enhance its predicting values.
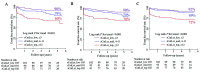
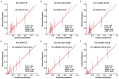
Methods: The rCatLet score was calculated retrospectively in 308 consecutively enrolled patients with AMI. Primary endpoint, major adverse cardiac or cerebrovascular events (MACCE) including all-cause mortality, non-fatal AMI, transient ischemic attack/stroke, and ischemia-driven repeat revascularization, was stratified according to rCatLet score tertiles: rCatLet_low ≤3, rCatLet_mid 4-11, and rCatLet_top ≥12, respectively. Cross-validation confirmed a reasonably good agreement between the observed and predicted risks.
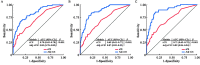
Results: Of 308 patients analyzed, the rates of MACCE, all-cause death, and cardiac death were 20.8%, 18.2%, and 15.3%, respectively. Kaplan-Meier curves for all endpoints showed increasing outcome events with the increasing tertiles of the rCatLet score, with P values <0.001 on trend test. For MACCE, all-cause death, and cardiac death, the area under the curves (AUCs) of the rCatLet score were 0.70 (95% confidence intervals [CI]: 0.63-0.78), 0.69 (95% CI: 0.61-0.77), and 0.71 (95% CI: 0.63-0.79), respectively; the AUCs of the CVs-adjusted rCatLet score models were 0.83 (95% CI: 0.78-0.89), 0.87 (95% CI: 0.82-0.92), and 0.89 (95% CI: 0.84-0.94), respectively. The performance of CVs-adjusted rCatLet score was significantly better than the stand-alone rCatLet score in terms of outcome predictions.
Conclusion: The rCatLet score has a predicting value for clinical outcomes for AMI patients and the incorporation of the three CVs into the rCatLet score will enhance its predicting ability.
Trial registration: http://www.chictr.org.cn , ChiCTR-POC-17013536.
Copyright © 2023 The Chinese Medical Association, produced by Wolters Kluwer, Inc. under the CC-BY-NC-ND license.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Predictive Value of the CatLet Scoring System for Long-Term Prognosis After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients With Chronic Coronary Syndrome.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2025 Feb;105(2):283-291. doi: 10.1002/ccd.31191. Epub 2024 Nov 6. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2025. PMID: 39506497
-
The CatLet score and outcome prediction in acute myocardial infarction for patients undergoing primary percutaneous intervention: A proof-of-concept study.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2020 Sep 1;96(3):E220-E229. doi: 10.1002/ccd.28724. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2020. PMID: 31943728
-
Age, Serum Creatinine, and Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Improved the Performance of the CatLet Angiographic Scoring System in Terms of Outcome Predictions for Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Median 4.3-Year Follow-Up Study.Cardiology. 2021;146(6):690-697. doi: 10.1159/000515759. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Cardiology. 2021. PMID: 34464951
-
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention vs Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting in Patients With Left Main Coronary Artery Stenosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Cardiol. 2017 Oct 1;2(10):1079-1088. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2017.2895. JAMA Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28903139 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of multivessel vs culprit lesion-only percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock: Evidence from an updated meta-analysis.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2019 Jul 1;94(1):70-81. doi: 10.1002/ccd.28062. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2019. PMID: 30593731
Cited by
-
Percutaneous coronary intervention vs . medical therapy in patients on dialysis with coronary artery disease in China.Chin Med J (Engl). 2025 Feb 5;138(3):301-310. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003295. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Chin Med J (Engl). 2025. PMID: 39317971 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of left ventricular ejection fraction in high-risk percutaneous coronary interventions.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Feb 2;11:1342409. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1342409. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38370154 Free PMC article.
-
Catlet scoring system as a new predictor for in-stent restenosis in patients with chronic coronary artery disease undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention with drug-eluting stent.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2025 Jan 29;20(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s13019-025-03349-2. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2025. PMID: 39881392 Free PMC article.
-
Coronary Artery Tree Description and Lesion Evaluation (CatLet) score for functional evaluation of coronary stenosis: a comparison study with pressure wire fractional flow reserve.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Apr 3;14(4):2857-2869. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-1635. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 38617154 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parikh PB, Kirtane AJ, Moses JW. Management of multivessel coronary artery disease. Panminerva Med 2013;55: 311–326. - PubMed
-
- Sorajja P Gersh BJ Cox DA McLaughlin MG Zimetbaum P Costantini C, et al. . Impact of multivessel disease on reperfusion success and clinical outcomes in patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention for acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J 2007;28: 1709–1716. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehm184. - PubMed
-
- Braga CG Cid-Alvarez AB Diéguez AR Alvarez BA Otero DL Sánchez RO, et al. . Prognostic impact of residual SYNTAX score in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction and multivessel disease: Analysis of an 8-year all-comers registry. Int J Cardiol 2017;243: 21–26. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.04.054. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

