The Role of Inflammation in the Initiation and Progression of Myeloid Neoplasms
- PMID: 37052531
- PMCID: PMC10320626
- DOI: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-22-0176
The Role of Inflammation in the Initiation and Progression of Myeloid Neoplasms
Abstract
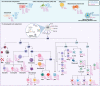
Myeloid malignancies are devastating hematologic cancers with limited therapeutic options. Inflammation is emerging as a novel driver of myeloid malignancy, with important implications for tumor composition, immune response, therapeutic options, and patient survival. Here, we discuss the role of inflammation in normal and malignant hematopoiesis, from clonal hematopoiesis to full-blown myeloid leukemia. We discuss how inflammation shapes clonal output from hematopoietic stem cells, how inflammation alters the immune microenvironment in the bone marrow, and novel therapies aimed at targeting inflammation in myeloid disease.
Significance: Inflammation is emerging as an important factor in myeloid malignancies. Understanding the role of inflammation in myeloid transformation, and the interplay between inflammation and other drivers of leukemogenesis, may yield novel avenues for therapy.
©2023 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures




References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011;144:646–74. - PubMed
-
- Denk D, Greten FR. Inflammation: the incubator of the tumor microenvironment. Trends Cancer 2022;8:901–14. - PubMed
-
- Bardou M, Barkun AN, Martel M. Obesity and colorectal cancer. Gut 2013;62:933–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

