Clinical Importance of the lncRNA NEAT1 in Cancer Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
- PMID: 37053197
- PMCID: PMC10330151
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-3714
Clinical Importance of the lncRNA NEAT1 in Cancer Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
Abstract
Purpose: mAbs targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint are powerful tools to improve the survival of patients with cancer. Understanding the molecular basis of clinical response to these treatments is critical to identify patients who can benefit from this immunotherapy. In this study, we investigated long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) expression in patients with cancer treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy.
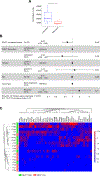
Experimental design: lncRNA expression profile was analyzed in one cohort of patients with melanoma and two independent cohorts of patients with glioblastoma (GBM) undergoing anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy. Single-cell RNA-sequencing analyses were performed to evaluate lncRNA expression in tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating immune cells.
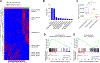
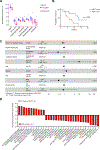
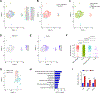
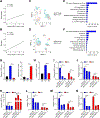
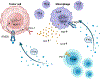
Results: We identified the lncRNA NEAT1 as commonly upregulated between patients with melanoma with complete therapeutic response and patients with GBM with longer survival following anti-PD-1/PD-L1 treatment. Gene set enrichment analyses revealed that NEAT1 expression was strongly associated with the IFNγ pathways, along with downregulation of cell-cycle-related genes. Single-cell RNA-sequencing analyses revealed NEAT1 expression across multiple cell types within the GBM microenvironment, including tumor cells, macrophages, and T cells. High NEAT1 expression levels in tumor cells correlated with increased infiltrating macrophages and microglia. In these tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells, we found that NEAT1 expression was linked to enrichment in TNFα/NFκB signaling pathway genes. Silencing NEAT1 suppressed M1 macrophage polarization and reduced the expression of TNFα and other inflammatory cytokines.
Conclusions: These findings suggest an association between NEAT1 expression and patient response to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy in melanoma and GBM and have important implications for the role of lncRNAs in the tumor microenvironment.
©2023 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest:
Marco Mineo and E. Antonio Chiocca are inventors on a patent application covering the use of
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

