NETs-Induced Thrombosis Impacts on Cardiovascular and Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 37053273
- PMCID: PMC10377271
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.321750
NETs-Induced Thrombosis Impacts on Cardiovascular and Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
Arterial and venous thrombosis constitute a major source of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Association between thrombotic complications and cardiovascular and other chronic inflammatory diseases are well described. Inflammation and subsequent initiation of thrombotic events, termed immunothrombosis, also receive growing attention but are still incompletely understood. Nevertheless, the clinical relevance of aberrant immunothrombosis, referred to as thromboinflammation, is evident by an increased risk of thrombosis and cardiovascular events in patients with inflammatory or infectious diseases. Proinflammatory mediators released from platelets, complement activation, and the formation of NETs (neutrophil extracellular traps) initiate and foster immunothrombosis. In this review, we highlight and discuss prominent and emerging interrelationships and functions between NETs and other mediators in immunothrombosis in cardiovascular disease. Also, with patients with chronic kidney disease suffering from increased cardiovascular and thrombotic risk, we summarize current knowledge on neutrophil phenotype, function, and NET formation in chronic kidney disease. In addition, we elaborate on therapeutic targeting of NETs-induced immunothrombosis. A better understanding of the functional relevance of antithrombotic mediators which do not increase bleeding risk may provide opportunities for successful therapeutic interventions to reduce thrombotic risk beyond current treatment options.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; inflammation; kidney; neutrophils; thrombosis.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

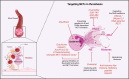
Similar articles
-
Platelets in the NETworks interweaving inflammation and thrombosis.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 1;13:953129. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.953129. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35979369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"The NET effect": Neutrophil extracellular traps-a potential key component of the dysregulated host immune response in sepsis.Crit Care. 2025 Feb 4;29(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s13054-025-05283-0. Crit Care. 2025. PMID: 39905519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heparin-Functionalized Adsorbents Eliminate Central Effectors of Immunothrombosis, including Platelet Factor 4, High-Mobility Group Box 1 Protein and Histones.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 5;23(3):1823. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031823. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163743 Free PMC article.
-
NETosis and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in COVID-19: Immunothrombosis and Beyond.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 2;13:838011. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.838011. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35309344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet-Neutrophil Crosstalk in Thrombosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 9;24(2):1266. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021266. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674781 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ACSL1 Aggravates Thromboinflammation by LPC/LPA Metabolic Axis in Hyperlipidemia Associated Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Mar;12(11):e2406359. doi: 10.1002/advs.202406359. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39853712 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational modifications in kidney diseases and associated cardiovascular risk.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024 Aug;20(8):495-512. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00837-x. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38664592 Review.
-
Multi-omics investigation of Porphyromonas gingivalis exacerbating acute kidney injury through the gut-kidney axis.mSystems. 2025 Feb 18;10(2):e0113624. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01136-24. Epub 2025 Jan 14. mSystems. 2025. PMID: 39807890 Free PMC article.
-
Association between advanced lung cancer inflammation index and chronic kidney disease: a cross-sectional study.Front Nutr. 2024 Oct 4;11:1430471. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1430471. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39430784 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory Mechanisms in a Neurovascular Disease: Cerebral Cavernous Malformation.Brain Sci. 2023 Sep 17;13(9):1336. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13091336. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37759937 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pircher J, Engelmann B, Massberg S, Schulz C. Platelet-neutrophil crosstalk in atherothrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 2019;119:1274–1282. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1692983 - PubMed
-
- Khandpur R, Carmona-Rivera C, Vivekanandan-Giri A, Gizinski A, Yalavarthi S, Knight JS, Friday S, Li S, Patel RM, Subramanian V, et al. . NETs are a source of citrullinated autoantigens and stimulate inflammatory responses in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5:178ra. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3005580 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pratesi F, Dioni I, Tommasi C, Alcaro MC, Paolini I, Barbetti F, Boscaro F, Panza F, Puxeddu I, Rovero P, et al. . Antibodies from patients with rheumatoid arthritis target citrullinated histone 4 contained in neutrophils extracellular traps. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73:1414–1422. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202765 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

