Distension evoked mucosal secretion in human and porcine colon in vitro
- PMID: 37053302
- PMCID: PMC10101454
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282732
Distension evoked mucosal secretion in human and porcine colon in vitro
Abstract
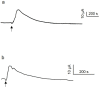
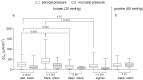
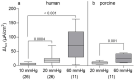
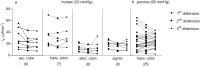
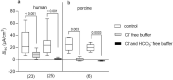
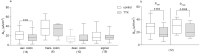
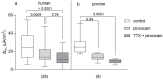
It was suggested that intestinal mucosal secretion is enhanced during muscle relaxation and contraction. Mechanisms of mechanically induced secretion have been studied in rodent species. We used voltage clamp Ussing technique to investigate, in human and porcine colonic tissue, secretion evoked by serosal (Pser) or mucosal (Pmuc) pressure application (2-60 mmHg) to induce distension into the mucosal or serosal compartment, respectively. In both species, Pser or Pmuc caused secretion due to Cl- and, in human colon, also HCO3- fluxes. In the human colon, responses were larger in proximal than distal regions. In porcine colon, Pmuc evoked larger responses than Pser whereas the opposite was the case in human colon. In both species, piroxicam revealed a strong prostaglandin (PG) dependent component. Pser and Pmuc induced secretion was tetrodotoxin (TTX) sensitive in porcine colon. In human colon, a TTX sensitive component was only revealed after piroxicam. However, synaptic blockade by ω-conotoxin GVIA reduced the response to mechanical stimuli. Secretion was induced by tensile rather than compressive forces as preventing distension by a filter inhibited the secretion. In conclusion, in both species, distension induced secretion was predominantly mediated by PGs and a rather small nerve dependent response involving mechanosensitive somata and synapses.
Copyright: © 2023 Elfers et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests:The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of inflammatory mediators on electrolyte transport across the porcine distal colon epithelium.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jan;264(1):61-6. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993. PMID: 8093732
-
Substance P-evoked Cl(-) secretion in guinea pig distal colonic epithelia: interaction with PGE(2).Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002 Aug;283(2):G347-56. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00504.2001. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12121882
-
Role of prostaglandins and enteric nerves in Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin (STa)-induced intestinal secretion in pigs.Am J Vet Res. 1996 Feb;57(2):211-5. Am J Vet Res. 1996. PMID: 8633810
-
Histamine augments colonic secretion in guinea pig distal colon.Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 1):G432-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.258.3.G432. Am J Physiol. 1990. PMID: 1969234
-
Regulation of ion transport in the porcine intestinal tract by enteric neurotransmitters and hormones.Comp Biochem Physiol A Physiol. 1997 Oct;118(2):309-17. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9629(96)00311-8. Comp Biochem Physiol A Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9366062 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional and Structural Investigation of Myenteric Neurons in the Human Colon.Gastro Hep Adv. 2024 Aug 24;4(1):100537. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2024.08.016. eCollection 2025. Gastro Hep Adv. 2024. PMID: 39790245 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

